| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We have defined momentum to be the product of mass and velocity. Therefore, if an object’s velocity should change (due to the application of a force on the object), then necessarily, its momentum changes as well. This indicates a connection between momentum and force. The purpose of this section is to explore and describe that connection.
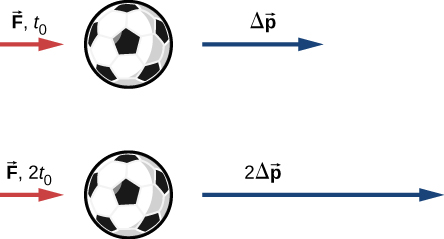
Suppose you apply a force on a free object for some amount of time. Clearly, the larger the force, the larger the object’s change of momentum will be. Alternatively, the more time you spend applying this force, again the larger the change of momentum will be, as depicted in [link] . The amount by which the object’s motion changes is therefore proportional to the magnitude of the force, and also to the time interval over which the force is applied.
Mathematically, if a quantity is proportional to two (or more) things, then it is proportional to the product of those things. The product of a force and a time interval (over which that force acts) is called impulse , and is given the symbol
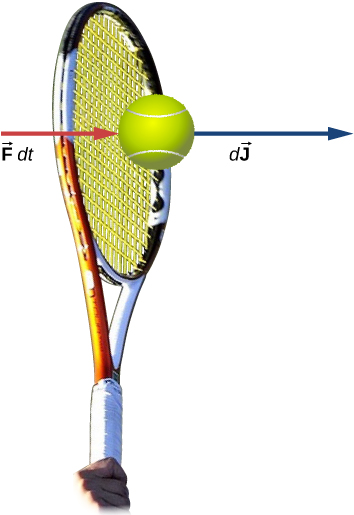
Let be the force applied to an object over some differential time interval dt ( [link] ). The resulting impulse on the object is defined as
The total impulse over the interval is
[link] and [link] together say that when a force is applied for an infinitesimal time interval dt , it causes an infinitesimal impulse , and the total impulse given to the object is defined to be the sum (integral) of all these infinitesimal impulses.
To calculate the impulse using [link] , we need to know the force function F ( t ), which we often don’t. However, a result from calculus is useful here: Recall that the average value of a function over some interval is calculated by
where . Applying this to the time-dependent force function, we obtain
Therefore, from [link] ,
The idea here is that you can calculate the impulse on the object even if you don’t know the details of the force as a function of time; you only need the average force. In fact, though, the process is usually reversed: You determine the impulse (by measurement or calculation) and then calculate the average force that caused that impulse.
To calculate the impulse, a useful result follows from writing the force in [link] as :
For a constant force , this simplifies to
That is,

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?