| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Our study of kinetic energy showed that a complete understanding of an object’s motion must include both its mass and its velocity ( ). However, as powerful as this concept is, it does not include any information about the direction of the moving object’s velocity vector. We’ll now define a physical quantity that includes direction.
Like kinetic energy, this quantity includes both mass and velocity; like kinetic energy, it is a way of characterizing the “quantity of motion” of an object. It is given the name momentum (from the Latin word movimentum , meaning “movement”), and it is represented by the symbol p .
The momentum p of an object is the product of its mass and its velocity:

As shown in [link] , momentum is a vector quantity (since velocity is). This is one of the things that makes momentum useful and not a duplication of kinetic energy. It is perhaps most useful when determining whether an object’s motion is difficult to change ( [link] ) or easy to change ( [link] ).

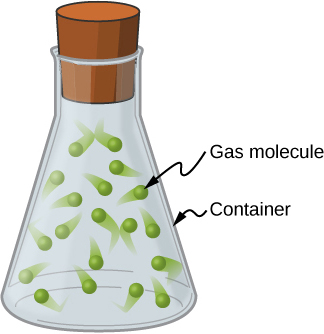
Unlike kinetic energy, momentum depends equally on an object’s mass and velocity. For example, as you will learn when you study thermodynamics, the average speed of an air molecule at room temperature is approximately 500 m/s, with an average molecular mass of ; its momentum is thus
For comparison, a typical automobile might have a speed of only 15 m/s, but a mass of 1400 kg, giving it a momentum of
These momenta are different by 27 orders of magnitude, or a factor of a billion billion billion!
An object that has a small mass and an object that has a large mass have the same momentum. Which object has the largest kinetic energy?
Since , then if the momentum is fixed, the object with smaller mass has more kinetic energy.
An object that has a small mass and an object that has a large mass have the same kinetic energy. Which mass has the largest momentum?
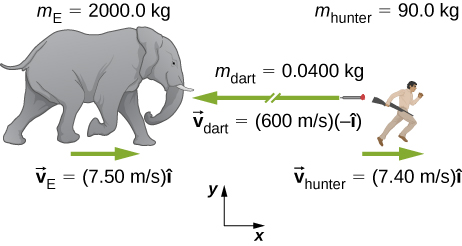
An elephant and a hunter are having a confrontation.
A skater of mass 40 kg is carrying a box of mass 5 kg. The skater has a speed of 5 m/s with respect to the floor and is gliding without any friction on a smooth surface.
a. magnitude: b. same as a.
A car of mass 2000 kg is moving with a constant velocity of 10 m/s due east. What is the momentum of the car?
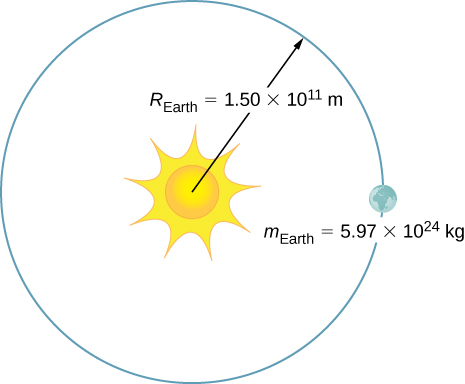
The mass of Earth is and its orbital radius is an average of . Calculate the magnitude of its average linear momentum.
If a rainstorm drops 1 cm of rain over an area of 10 km 2 in the period of 1 hour, what is the momentum of the rain that falls in one second? Assume the terminal velocity of a raindrop is 10 m/s.
What is the average momentum of an avalanche that moves a 40-cm-thick layer of snow over an area of 100 m by 500 m over a distance of 1 km down a hill in 5.5 s? Assume a density of 350 kg/m 3 for the snow.
What is the average momentum of a 70.0-kg sprinter who runs the 100-m dash in 9.65 s?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?