| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In an iconic movie scene, Forrest Gump runs around the country. If he is running at a constant speed of 3 m/s, would it take him more or less energy to run uphill or downhill and why?
In the movie Monty Python and the Holy Grail a cow is catapulted from the top of a castle wall over to the people down below. The gravitational potential energy is set to zero at ground level. The cow is launched from a spring of spring constant that is expanded 0.5 m from equilibrium. If the castle is 9.1 m tall and the mass of the cow is 110 kg, (a) what is the gravitational potential energy of the cow at the top of the castle? (b) What is the elastic spring energy of the cow before the catapult is released? (c) What is the speed of the cow right before it lands on the ground?
a. ; b. ; c. 14 m/s
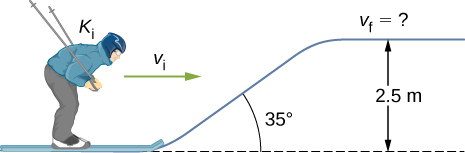
A 60.0-kg skier with an initial speed of 12.0 m/s coasts up a 2.50-m high rise as shown. Find her final speed at the top, given that the coefficient of friction between her skis and the snow is 0.80.
(a) How high a hill can a car coast up (engines disengaged) if work done by friction is negligible and its initial speed is 110 km/h? (b) If, in actuality, a 750-kg car with an initial speed of 110 km/h is observed to coast up a hill to a height 22.0 m above its starting point, how much thermal energy was generated by friction? (c) What is the average force of friction if the hill has a slope of above the horizontal?
a. 47.6 m; b. ; c. 373 N
A subway train is brought to a stop from a speed of 0.500 m/s in 0.400 m by a large spring bumper at the end of its track. What is the spring constant k of the spring?
A pogo stick has a spring with a spring constant of which can be compressed 12.0 cm. To what maximum height from the uncompressed spring can a child jump on the stick using only the energy in the spring, if the child and stick have a total mass of 40 kg?
33.9 cm
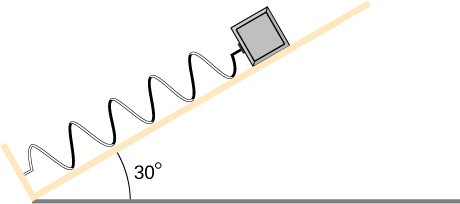
A block of mass 500 g is attached to a spring of spring constant 80 N/m (see the following figure). The other end of the spring is attached to a support while the mass rests on a rough surface with a coefficient of friction of 0.20 that is inclined at angle of The block is pushed along the surface till the spring compresses by 10 cm and is then released from rest. (a) How much potential energy was stored in the block-spring-support system when the block was just released? (b) Determine the speed of the block when it crosses the point when the spring is neither compressed nor stretched. (c) Determine the position of the block where it just comes to rest on its way up the incline.
A block of mass 200 g is attached at the end of a massless spring of spring constant 100 N/cm. The other end of the spring is attached to the ceiling and the mass is brought to rest. Let us mark this point as O . Suppose, this point is taken to be the zero of the potential energy of the block, both from the weight and the spring force. The mass hangs freely and the spring is in a stretched state. The block is then pulled downward by another 5.00 cm and released from rest. (a) What is the net potential energy of the block at the instant the block is at the lowest point? (b) What is the net potential energy of the block at the instant the block returns to the point marked O ? (c) What is the speed of the block as it crosses the point marked O ? (d) How high above the point marked O does the block rise before coming to rest again?
a. 0.0269 J; b. ; c. 1.11 m/s; d. 4.96 cm

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?