| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We have thus far considered force as a push or a pull; however, if you think about it, you realize that no push or pull ever occurs by itself. When you push on a wall, the wall pushes back on you. This brings us to Newton’s third law .
Whenever one body exerts a force on a second body, the first body experiences a force that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force that it exerts. Mathematically, if a body A exerts a force on body B , then B simultaneously exerts a force on A , or in vector equation form,
Newton’s third law represents a certain symmetry in nature: Forces always occur in pairs, and one body cannot exert a force on another without experiencing a force itself. We sometimes refer to this law loosely as “action-reaction,” where the force exerted is the action and the force experienced as a consequence is the reaction. Newton’s third law has practical uses in analyzing the origin of forces and understanding which forces are external to a system.
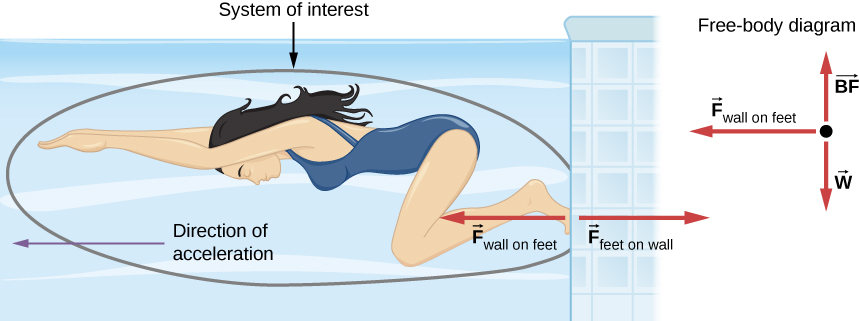
We can readily see Newton’s third law at work by taking a look at how people move about. Consider a swimmer pushing off the side of a pool ( [link] ). She pushes against the wall of the pool with her feet and accelerates in the direction opposite that of her push. The wall has exerted an equal and opposite force on the swimmer. You might think that two equal and opposite forces would cancel, but they do not because they act on different systems . In this case, there are two systems that we could investigate: the swimmer and the wall. If we select the swimmer to be the system of interest, as in the figure, then is an external force on this system and affects its motion. The swimmer moves in the direction of this force. In contrast, the force acts on the wall, not on our system of interest. Thus, does not directly affect the motion of the system and does not cancel The swimmer pushes in the direction opposite that in which she wishes to move. The reaction to her push is thus in the desired direction. In a free-body diagram, such as the one shown in [link] , we never include both forces of an action-reaction pair; in this case, we only use , not .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?