| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Experience suggests that an object at rest remains at rest if left alone and that an object in motion tends to slow down and stop unless some effort is made to keep it moving. However, Newton’s first law gives a deeper explanation of this observation.
A body at rest remains at rest or, if in motion, remains in motion at constant velocity unless acted on by a net external force.
Note the repeated use of the verb “remains.” We can think of this law as preserving the status quo of motion. Also note the expression “constant velocity;” this means that the object maintains a path along a straight line, since neither the magnitude nor the direction of the velocity vector changes. We can use [link] to consider the two parts of Newton’s first law.

Rather than contradicting our experience, Newton’s first law says that there must be a cause for any change in velocity (a change in either magnitude or direction) to occur. This cause is a net external force, which we defined earlier in the chapter. An object sliding across a table or floor slows down due to the net force of friction acting on the object. If friction disappears, will the object still slow down?
The idea of cause and effect is crucial in accurately describing what happens in various situations. For example, consider what happens to an object sliding along a rough horizontal surface. The object quickly grinds to a halt. If we spray the surface with talcum powder to make the surface smoother, the object slides farther. If we make the surface even smoother by rubbing lubricating oil on it, the object slides farther yet. Extrapolating to a frictionless surface and ignoring air resistance, we can imagine the object sliding in a straight line indefinitely. Friction is thus the cause of slowing (consistent with Newton’s first law). The object would not slow down if friction were eliminated.
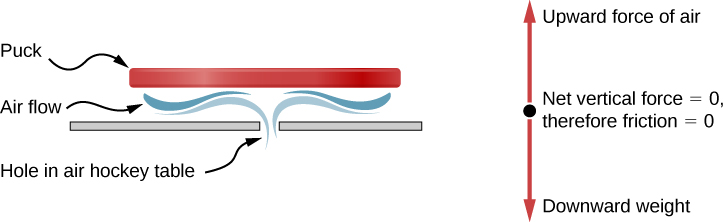
Consider an air hockey table ( [link] ). When the air is turned off, the puck slides only a short distance before friction slows it to a stop. However, when the air is turned on, it creates a nearly frictionless surface, and the puck glides long distances without slowing down. Additionally, if we know enough about the friction, we can accurately predict how quickly the object slows down.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?