| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Uniform circular motion is a specific type of motion in which an object travels in a circle with a constant speed. For example, any point on a propeller spinning at a constant rate is executing uniform circular motion. Other examples are the second, minute, and hour hands of a watch. It is remarkable that points on these rotating objects are actually accelerating, although the rotation rate is a constant. To see this, we must analyze the motion in terms of vectors.
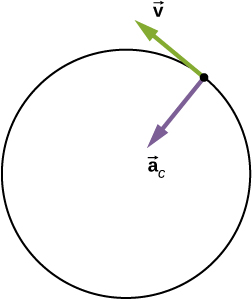
In one-dimensional kinematics, objects with a constant speed have zero acceleration. However, in two- and three-dimensional kinematics, even if the speed is a constant, a particle can have acceleration if it moves along a curved trajectory such as a circle. In this case the velocity vector is changing, or This is shown in [link] . As the particle moves counterclockwise in time on the circular path, its position vector moves from to The velocity vector has constant magnitude and is tangent to the path as it changes from to changing its direction only. Since the velocity vector is perpendicular to the position vector the triangles formed by the position vectors and and the velocity vectors and are similar. Furthermore, since and the two triangles are isosceles. From these facts we can make the assertion
or

We can find the magnitude of the acceleration from
The direction of the acceleration can also be found by noting that as and therefore approach zero, the vector approaches a direction perpendicular to In the limit is perpendicular to Since is tangent to the circle, the acceleration points toward the center of the circle. Summarizing, a particle moving in a circle at a constant speed has an acceleration with magnitude
The direction of the acceleration vector is toward the center of the circle ( [link] ). This is a radial acceleration and is called the centripetal acceleration , which is why we give it the subscript c. The word centripetal comes from the Latin words centrum (meaning “center”) and petere (meaning to seek”), and thus takes the meaning “center seeking.”

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?