| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Projectile motion is the motion of an object thrown or projected into the air, subject only to acceleration as a result of gravity. The applications of projectile motion in physics and engineering are numerous. Some examples include meteors as they enter Earth’s atmosphere, fireworks, and the motion of any ball in sports. Such objects are called projectiles and their path is called a trajectory . The motion of falling objects as discussed in Motion Along a Straight Line is a simple one-dimensional type of projectile motion in which there is no horizontal movement. In this section, we consider two-dimensional projectile motion, and our treatment neglects the effects of air resistance.
The most important fact to remember here is that motions along perpendicular axes are independent and thus can be analyzed separately. We discussed this fact in Displacement and Velocity Vectors , where we saw that vertical and horizontal motions are independent. The key to analyzing two-dimensional projectile motion is to break it into two motions: one along the horizontal axis and the other along the vertical. (This choice of axes is the most sensible because acceleration resulting from gravity is vertical; thus, there is no acceleration along the horizontal axis when air resistance is negligible.) As is customary, we call the horizontal axis the x -axis and the vertical axis the y -axis. It is not required that we use this choice of axes; it is simply convenient in the case of gravitational acceleration. In other cases we may choose a different set of axes. [link] illustrates the notation for displacement, where we define to be the total displacement, and and are its component vectors along the horizontal and vertical axes, respectively. The magnitudes of these vectors are s , x , and y .
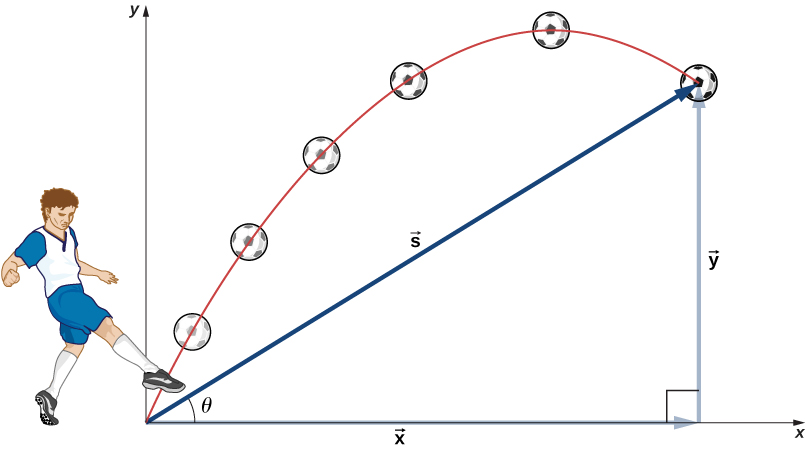
To describe projectile motion completely, we must include velocity and acceleration, as well as displacement. We must find their components along the x- and y -axes. Let’s assume all forces except gravity (such as air resistance and friction, for example) are negligible. Defining the positive direction to be upward, the components of acceleration are then very simple:
Because gravity is vertical, If this means the initial velocity in the x direction is equal to the final velocity in the x direction, or With these conditions on acceleration and velocity, we can write the kinematic [link] through [link] for motion in a uniform gravitational field, including the rest of the kinematic equations for a constant acceleration from Motion with Constant Acceleration . The kinematic equations for motion in a uniform gravitational field become kinematic equations with

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?