| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In Applications of Newton’s Laws , which introduced the concept of friction, we saw that an object sliding across the floor with an initial velocity and no applied force comes to rest due to the force of friction. Friction depends on the types of materials in contact and is proportional to the normal force. We also discussed drag and air resistance in that same chapter. We explained that at low speeds, the drag is proportional to the velocity, whereas at high speeds, drag is proportional to the velocity squared. In this section, we introduce the forces of friction that act on fluids in motion. For example, a fluid flowing through a pipe is subject to resistance, a type of friction, between the fluid and the walls. Friction also occurs between the different layers of fluid. These resistive forces affect the way the fluid flows through the pipe.
When you pour yourself a glass of juice, the liquid flows freely and quickly. But if you pour maple syrup on your pancakes, that liquid flows slowly and sticks to the pitcher. The difference is fluid friction, both within the fluid itself and between the fluid and its surroundings. We call this property of fluids viscosity . Juice has low viscosity, whereas syrup has high viscosity.
The precise definition of viscosity is based on laminar, or nonturbulent, flow. [link] shows schematically how laminar and turbulent flow differ. When flow is laminar, layers flow without mixing. When flow is turbulent, the layers mix, and significant velocities occur in directions other than the overall direction of flow.
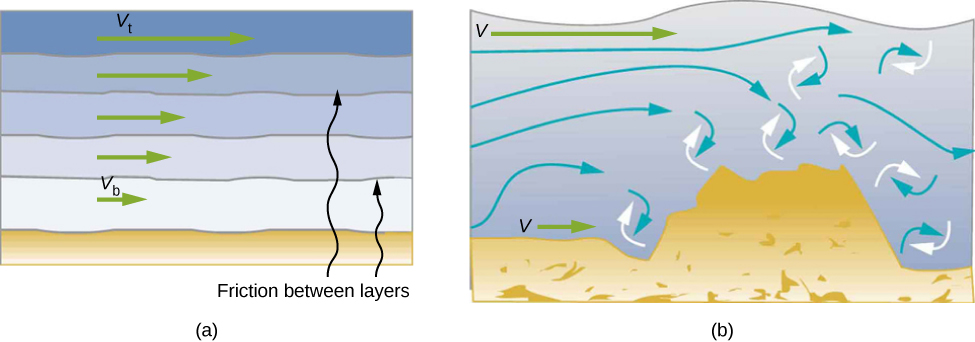
Turbulence is a fluid flow in which layers mix together via eddies and swirls. It has two main causes. First, any obstruction or sharp corner, such as in a faucet, creates turbulence by imparting velocities perpendicular to the flow. Second, high speeds cause turbulence . The drag between adjacent layers of fluid and between the fluid and its surroundings can form swirls and eddies if the speed is great enough. In [link] , the speed of the accelerating smoke reaches the point that it begins to swirl due to the drag between the smoke and the surrounding air.


Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?