| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Matter most commonly exists as a solid, liquid, or gas; these states are known as the three common phases of matter . We will look at each of these phases in detail in this section.
Solids are rigid and have specific shapes and definite volumes. The atoms or molecules in a solid are in close proximity to each other, and there is a significant force between these molecules. Solids will take a form determined by the nature of these forces between the molecules. Although true solids are not incompressible, it nevertheless requires a large force to change the shape of a solid. In some cases, the force between molecules can cause the molecules to organize into a lattice as shown in [link] . The structure of this three-dimensional lattice is represented as molecules connected by rigid bonds (modeled as stiff springs), which allow limited freedom for movement. Even a large force produces only small displacements in the atoms or molecules of the lattice, and the solid maintains its shape. Solids also resist shearing forces. (Shearing forces are forces applied tangentially to a surface, as described in Static Equilibrium and Elasticity .)
Liquids and gases are considered to be fluids because they yield to shearing forces, whereas solids resist them. Like solids, the molecules in a liquid are bonded to neighboring molecules, but possess many fewer of these bonds. The molecules in a liquid are not locked in place and can move with respect to each other. The distance between molecules is similar to the distances in a solid, and so liquids have definite volumes, but the shape of a liquid changes, depending on the shape of its container. Gases are not bonded to neighboring atoms and can have large separations between molecules. Gases have neither specific shapes nor definite volumes, since their molecules move to fill the container in which they are held ( [link] ).
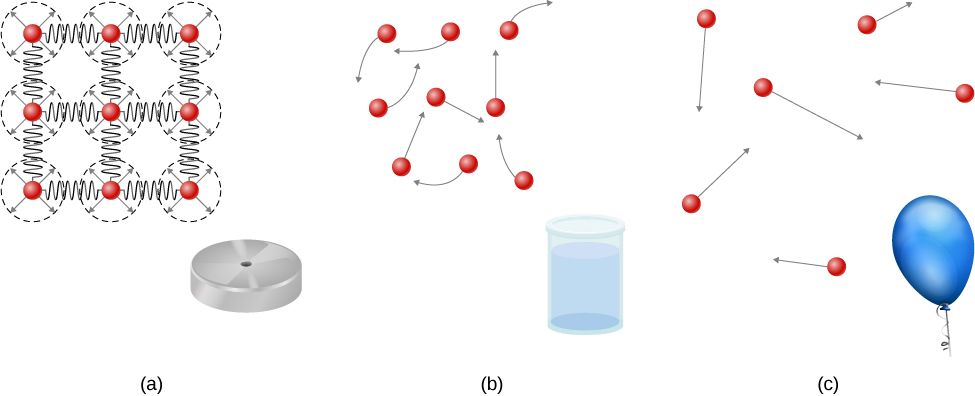
Liquids deform easily when stressed and do not spring back to their original shape once a force is removed. This occurs because the atoms or molecules in a liquid are free to slide about and change neighbors. That is, liquids flow (so they are a type of fluid), with the molecules held together by mutual attraction. When a liquid is placed in a container with no lid, it remains in the container. Because the atoms are closely packed, liquids, like solids, resist compression; an extremely large force is necessary to change the volume of a liquid.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?