| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A particle of mass 5.0 kg has position vector at a particular instant of time when its velocity is with respect to the origin. (a) What is the angular momentum of the particle? (b) If a force acts on the particle at this instant, what is the torque about the origin?
a.
;
b.
Use the right-hand rule to determine the directions of the angular momenta about the origin of the particles as shown below. The z- axis is out of the page.
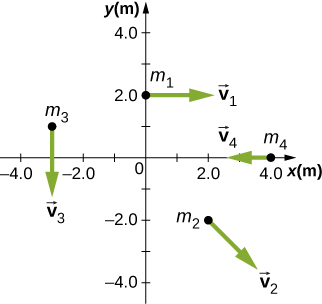
Suppose the particles in the preceding problem have masses . The velocities of the particles are , , , . (a) Calculate the angular momentum of each particle about the origin. (b) What is the total angular momentum of the four-particle system about the origin?
a.
,
,
; b.
Two particles of equal mass travel with the same speed in opposite directions along parallel lines separated by a distance d . Show that the angular momentum of this two-particle system is the same no matter what point is used as the reference for calculating the angular momentum.
An airplane of mass flies horizontally at an altitude of 10 km with a constant speed of 250 m/s relative to Earth. (a) What is the magnitude of the airplane’s angular momentum relative to a ground observer directly below the plane? (b) Does the angular momentum change as the airplane flies along its path?
a. ; b. No, the angular momentum stays the same since the cross-product involves only the perpendicular distance from the plane to the ground no matter where it is along its path.
At a particular instant, a 1.0-kg particle’s position is , its velocity is , and the force on it is . (a) What is the angular momentum of the particle about the origin? (b) What is the torque on the particle about the origin? (c) What is the time rate of change of the particle’s angular momentum at this instant?
A particle of mass m is dropped at the point and falls vertically in Earth’s gravitational field (a) What is the expression for the angular momentum of the particle around the z -axis, which points directly out of the page as shown below? (b) Calculate the torque on the particle around the z -axis. (c) Is the torque equal to the time rate of change of the angular momentum?

a.
;
b.
; c. yes
(a) Calculate the angular momentum of Earth in its orbit around the Sun. (b) Compare this angular momentum with the angular momentum of Earth about its axis.
A boulder of mass 20 kg and radius 20 cm rolls down a hill 15 m high from rest. What is its angular momentum when it is half way down the hill? (b) At the bottom?
a.
;
;
;
b.
;
A satellite is spinning at 6.0 rev/s. The satellite consists of a main body in the shape of a sphere of radius 2.0 m and mass 10,000 kg, and two antennas projecting out from the center of mass of the main body that can be approximated with rods of length 3.0 m each and mass 10 kg. The antenna’s lie in the plane of rotation. What is the angular momentum of the satellite?
A propeller consists of two blades each 3.0 m in length and mass 120 kg each. The propeller can be approximated by a single rod rotating about its center of mass. The propeller starts from rest and rotates up to 1200 rpm in 30 seconds at a constant rate. (a) What is the angular momentum of the propeller at (b) What is the torque on the propeller?
a.
;
;
;
;
;
b.
A pulsar is a rapidly rotating neutron star. The Crab nebula pulsar in the constellation Taurus has a period of , radius 10.0 km, and mass The pulsar’s rotational period will increase over time due to the release of electromagnetic radiation, which doesn’t change its radius but reduces its rotational energy. (a) What is the angular momentum of the pulsar? (b) Suppose the angular velocity decreases at a rate of . What is the torque on the pulsar?
The blades of a wind turbine are 30 m in length and rotate at a maximum rotation rate of 20 rev/min. (a) If the blades are 6000 kg each and the rotor assembly has three blades, calculate the angular momentum of the turbine at this rotation rate. (b) What is the torque require to rotate the blades up to the maximum rotation rate in 5 minutes?
a.
;
b.
A roller coaster has mass 3000.0 kg and needs to make it safely through a vertical circular loop of radius 50.0 m. What is the minimum angular momentum of the coaster at the bottom of the loop to make it safely through? Neglect friction on the track. Take the coaster to be a point particle.
A mountain biker takes a jump in a race and goes airborne. The mountain bike is travelling at 10.0 m/s before it goes airborne. If the mass of the front wheel on the bike is 750 g and has radius 35 cm, what is the angular momentum of the spinning wheel in the air the moment the bike leaves the ground?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?