| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Why does Earth keep on spinning? What started it spinning to begin with? Why doesn’t Earth’s gravitational attraction not bring the Moon crashing in toward Earth? And how does an ice skater manage to spin faster and faster simply by pulling her arms in? Why does she not have to exert a torque to spin faster?
The answer to these questions is that just as the total linear motion (momentum) in the universe is conserved, so is the total rotational motion conserved. We call the total rotational motion angular momentum, the rotational counterpart to linear momentum. In this chapter, we first define and then explore angular momentum from a variety of viewpoints. First, however, we investigate the angular momentum of a single particle. This allows us to develop angular momentum for a system of particles and for a rigid body.
[link] shows a particle at a position with linear momentum with respect to the origin. Even if the particle is not rotating about the origin, we can still define an angular momentum in terms of the position vector and the linear momentum.
The angular momentum of a particle is defined as the cross-product of and , and is perpendicular to the plane containing and
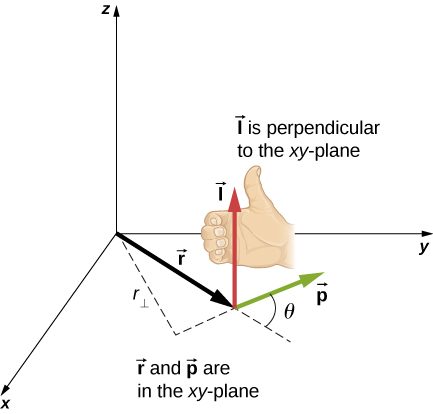
The intent of choosing the direction of the angular momentum to be perpendicular to the plane containing and is similar to choosing the direction of torque to be perpendicular to the plane of as discussed in Fixed-Axis Rotation . The magnitude of the angular momentum is found from the definition of the cross-product,
where is the angle between and The units of angular momentum are .
As with the definition of torque, we can define a lever arm that is the perpendicular distance from the momentum vector to the origin, With this definition, the magnitude of the angular momentum becomes
We see that if the direction of is such that it passes through the origin, then and the angular momentum is zero because the lever arm is zero. In this respect, the magnitude of the angular momentum depends on the choice of origin.
If we take the time derivative of the angular momentum, we arrive at an expression for the torque on the particle:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?