| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
and substituting this into Newton’s second law, , gives
We substitute known values to obtain
which yields
which is the acceleration parallel to the incline when there is 45.0 N of opposing friction.
Discussion
Since friction always opposes motion between surfaces, the acceleration is smaller when there is friction than when there is none. In fact, it is a general result that if friction on an incline is negligible, then the acceleration down the incline is , regardless of mass . This is related to the previously discussed fact that all objects fall with the same acceleration in the absence of air resistance. Similarly, all objects, regardless of mass, slide down a frictionless incline with the same acceleration (if the angle is the same).
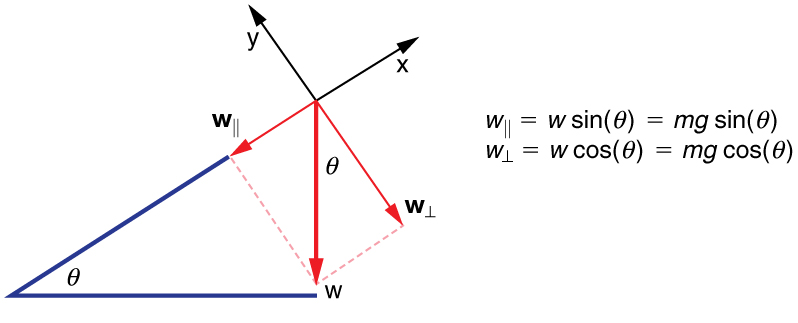
When an object rests on an incline that makes an angle with the horizontal, the force of gravity acting on the object is divided into two components: a force acting perpendicular to the plane, , and a force acting parallel to the plane, . The perpendicular force of weight, , is typically equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the normal force, . The force acting parallel to the plane, , causes the object to accelerate down the incline. The force of friction, , opposes the motion of the object, so it acts upward along the plane.
It is important to be careful when resolving the weight of the object into components. If the angle of the incline is at an angle to the horizontal, then the magnitudes of the weight components are
and
Instead of memorizing these equations, it is helpful to be able to determine them from reason. To do this, draw the right triangle formed by the three weight vectors. Notice that the angle of the incline is the same as the angle formed between and . Knowing this property, you can use trigonometry to determine the magnitude of the weight components:
To investigate how a force parallel to an inclined plane changes, find a rubber band, some objects to hang from the end of the rubber band, and a board you can position at different angles. How much does the rubber band stretch when you hang the object from the end of the board? Now place the board at an angle so that the object slides off when placed on the board. How much does the rubber band extend if it is lined up parallel to the board and used to hold the object stationary on the board? Try two more angles. What does this show?
A tension is a force along the length of a medium, especially a force carried by a flexible medium, such as a rope or cable. The word “tension ” comes from a Latin word meaning “to stretch.” Not coincidentally, the flexible cords that carry muscle forces to other parts of the body are called tendons . Any flexible connector, such as a string, rope, chain, wire, or cable, can exert pulls only parallel to its length; thus, a force carried by a flexible connector is a tension with direction parallel to the connector. It is important to understand that tension is a pull in a connector. In contrast, consider the phrase: “You can’t push a rope.” The tension force pulls outward along the two ends of a rope.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?