| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
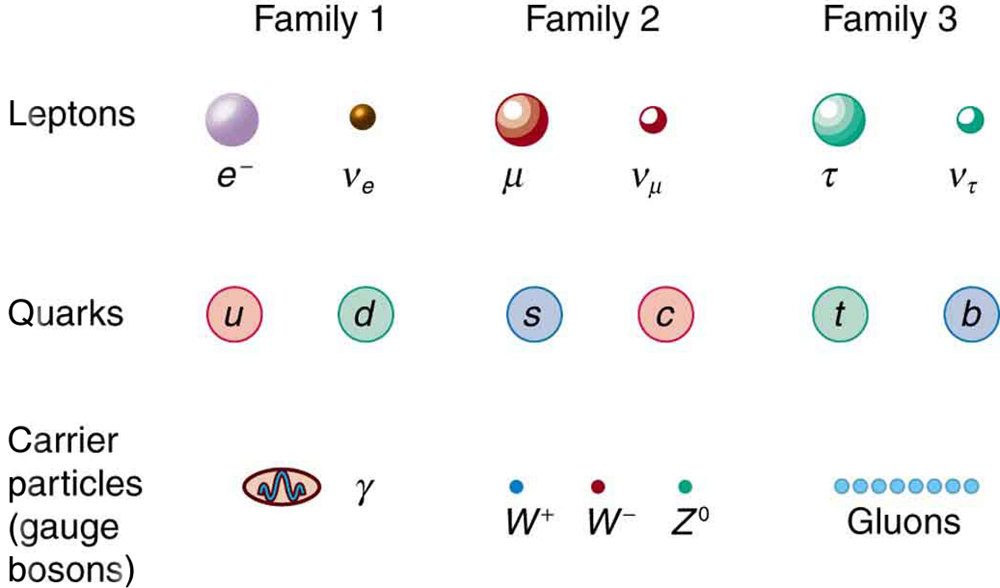
Fundamental particles are thought to be one of three types—leptons, quarks, or carrier particles. Each of those three types is further divided into three analogous families as illustrated in [link] . We have examined leptons and quarks in some detail. Each has six members (and their six antiparticles) divided into three analogous families. The first family is normal matter, of which most things are composed. The second is exotic, and the third more exotic and more massive than the second. The only stable particles are in the first family, which also has unstable members.
Always searching for symmetry and similarity, physicists have also divided the carrier particles into three families, omitting the graviton. Gravity is special among the four forces in that it affects the space and time in which the other forces exist and is proving most difficult to include in a Theory of Everything or TOE (to stub the pretension of such a theory). Gravity is thus often set apart. It is not certain that there is meaning in the groupings shown in [link] , but the analogies are tempting. In the past, we have been able to make significant advances by looking for analogies and patterns, and this is an example of one under current scrutiny. There are connections between the families of leptons, in that the decays into the and the into the e . Similarly for quarks, the higher families eventually decay into the lowest, leaving only u and d quarks. We have long sought connections between the forces in nature. Since these are carried by particles, we will explore connections between gluons, and , and photons as part of the search for unification of forces discussed in GUTs: The Unification of Forces ..
The quark flavor change takes place in decay. Does this mean that the reverse quark flavor change takes place in decay? Justify your response by writing the decay in terms of the quark constituents, noting that it looks as if a proton is converted into a neutron in decay.
Explain how the weak force can change strangeness by changing quark flavor.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?