| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
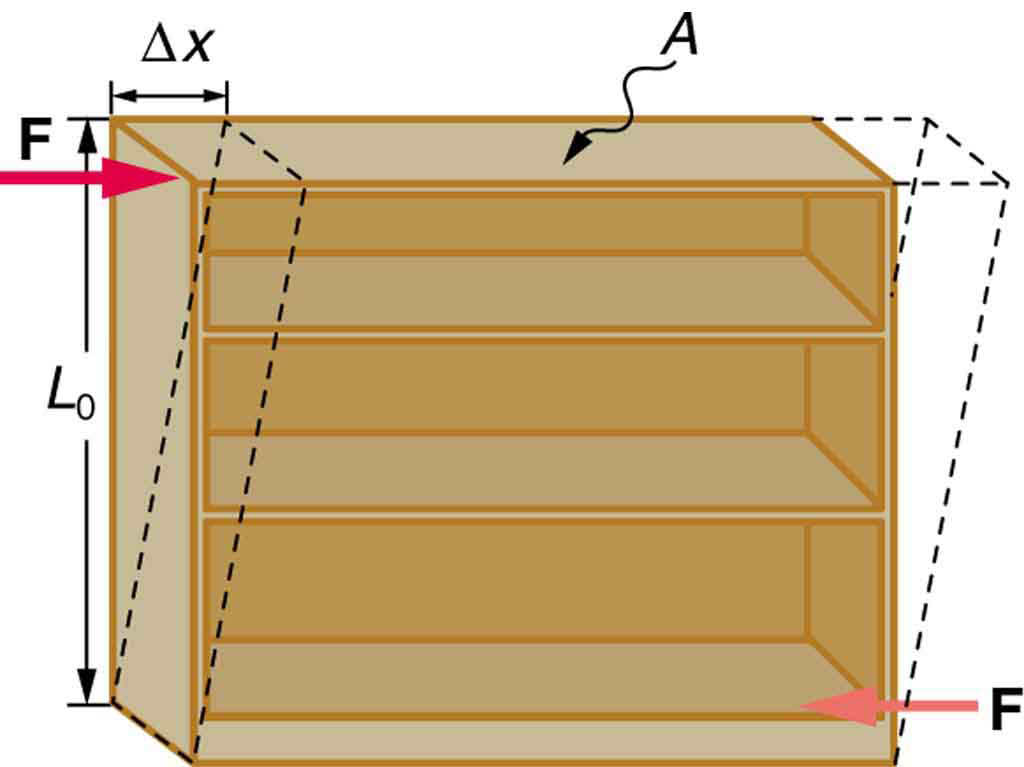
[link] illustrates what is meant by a sideways stress or a shearing force . Here the deformation is called and it is perpendicular to , rather than parallel as with tension and compression. Shear deformation behaves similarly to tension and compression and can be described with similar equations. The expression for shear deformation is
where is the shear modulus (see [link] ) and is the force applied perpendicular to and parallel to the cross-sectional area . Again, to keep the object from accelerating, there are actually two equal and opposite forces applied across opposite faces, as illustrated in [link] . The equation is logical—for example, it is easier to bend a long thin pencil (small ) than a short thick one, and both are more easily bent than similar steel rods (large ).
where is the shear modulus and is the force applied perpendicular to and parallel to the cross-sectional area .
Examination of the shear moduli in [link] reveals some telling patterns. For example, shear moduli are less than Young’s moduli for most materials. Bone is a remarkable exception. Its shear modulus is not only greater than its Young’s modulus, but it is as large as that of steel. This is why bones are so rigid.
The spinal column (consisting of 26 vertebral segments separated by discs) provides the main support for the head and upper part of the body. The spinal column has normal curvature for stability, but this curvature can be increased, leading to increased shearing forces on the lower vertebrae. Discs are better at withstanding compressional forces than shear forces. Because the spine is not vertical, the weight of the upper body exerts some of both. Pregnant women and people that are overweight (with large abdomens) need to move their shoulders back to maintain balance, thereby increasing the curvature in their spine and so increasing the shear component of the stress. An increased angle due to more curvature increases the shear forces along the plane. These higher shear forces increase the risk of back injury through ruptured discs. The lumbosacral disc (the wedge shaped disc below the last vertebrae) is particularly at risk because of its location.
The shear moduli for concrete and brick are very small; they are too highly variable to be listed. Concrete used in buildings can withstand compression, as in pillars and arches, but is very poor against shear, as might be encountered in heavily loaded floors or during earthquakes. Modern structures were made possible by the use of steel and steel-reinforced concrete. Almost by definition, liquids and gases have shear moduli near zero, because they flow in response to shearing forces.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?