| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We have noted that distance traveled can be greater than displacement. So average speed can be greater than average velocity, which is displacement divided by time. For example, if you drive to a store and return home in half an hour, and your car’s odometer shows the total distance traveled was 6 km, then your average speed was 12 km/h. Your average velocity, however, was zero, because your displacement for the round trip is zero. (Displacement is change in position and, thus, is zero for a round trip.) Thus average speed is not simply the magnitude of average velocity.
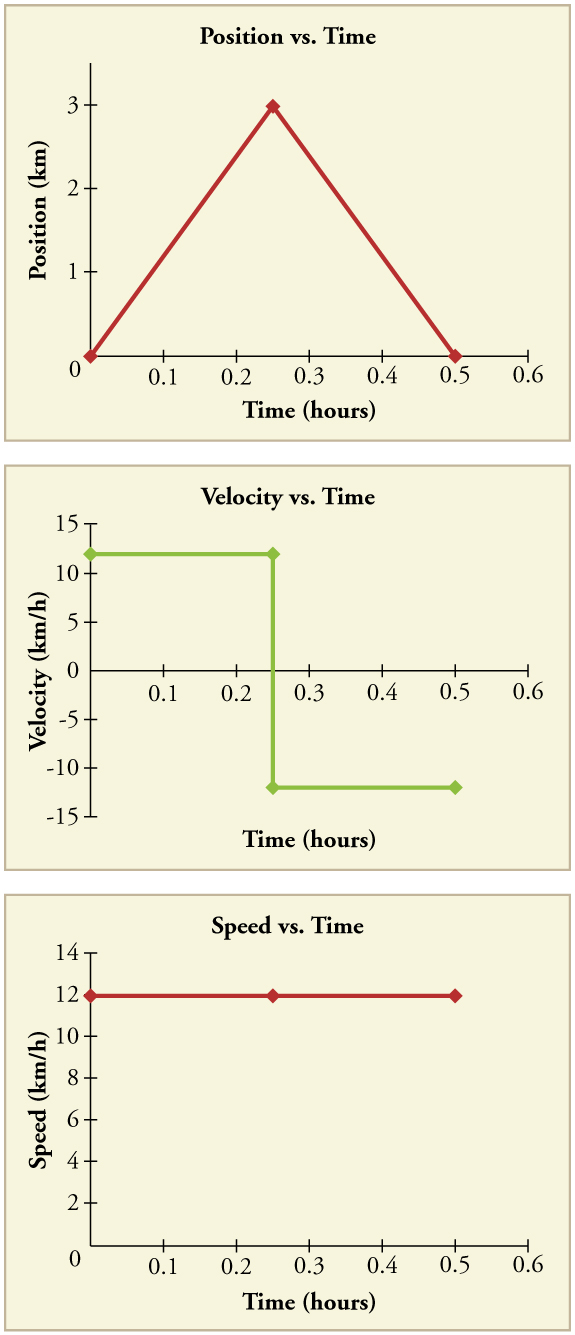
Another way of visualizing the motion of an object is to use a graph. A plot of position or of velocity as a function of time can be very useful. For example, for this trip to the store, the position, velocity, and speed-vs.-time graphs are displayed in [link] . (Note that these graphs depict a very simplified model of the trip. We are assuming that speed is constant during the trip, which is unrealistic given that we’ll probably stop at the store. But for simplicity’s sake, we will model it with no stops or changes in speed. We are also assuming that the route between the store and the house is a perfectly straight line.)
If you have spent much time driving, you probably have a good sense of speeds between about 10 and 70 miles per hour. But what are these in meters per second? What do we mean when we say that something is moving at 10 m/s? To get a better sense of what these values really mean, do some observations and calculations on your own:
A commuter train travels from Baltimore to Washington, DC, and back in 1 hour and 45 minutes. The distance between the two stations is approximately 40 miles. What is (a) the average velocity of the train, and (b) the average speed of the train in m/s?
(a) The average velocity of the train is zero because ; the train ends up at the same place it starts.
(b) The average speed of the train is calculated below. Note that the train travels 40 miles one way and 40 miles back, for a total distance of 80 miles.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?