| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Dynamics is the study of the forces that cause objects and systems to move. To understand this, we need a working definition of force. Our intuitive definition of force —that is, a push or a pull—is a good place to start. We know that a push or pull has both magnitude and direction (therefore, it is a vector quantity) and can vary considerably in each regard. For example, a cannon exerts a strong force on a cannonball that is launched into the air. In contrast, Earth exerts only a tiny downward pull on a flea. Our everyday experiences also give us a good idea of how multiple forces add. If two people push in different directions on a third person, as illustrated in [link] , we might expect the total force to be in the direction shown. Since force is a vector, it adds just like other vectors, as illustrated in [link] (a) for two ice skaters. Forces, like other vectors, are represented by arrows and can be added using the familiar head-to-tail method or by trigonometric methods. These ideas were developed in Two-Dimensional Kinematics .
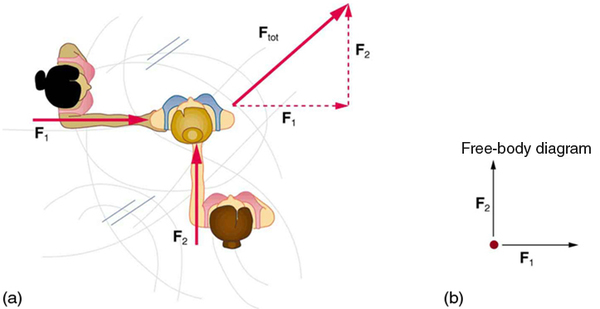
[link] (b) is our first example of a free-body diagram , which is a technique used to illustrate all the external forces acting on a body. The body is represented by a single isolated point (or free body), and only those forces acting on the body from the outside (external forces) are shown. (These forces are the only ones shown, because only external forces acting on the body affect its motion. We can ignore any internal forces within the body.) Free-body diagrams are very useful in analyzing forces acting on a system and are employed extensively in the study and application of Newton’s laws of motion.
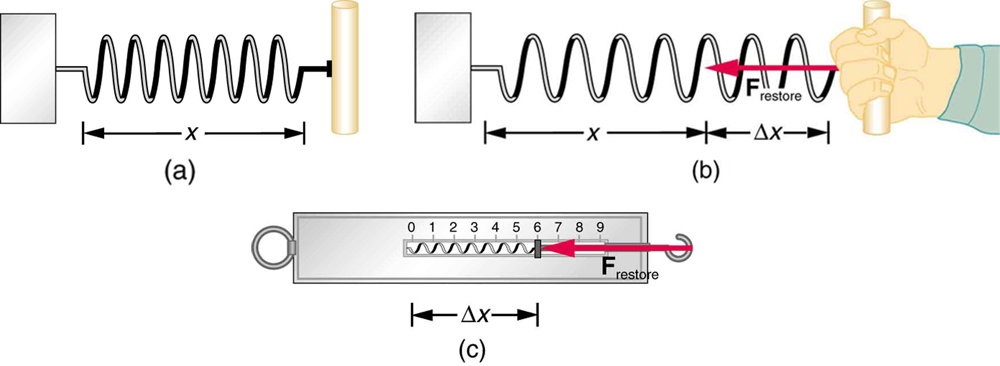
A more quantitative definition of force can be based on some standard force, just as distance is measured in units relative to a standard distance. One possibility is to stretch a spring a certain fixed distance, as illustrated in [link] , and use the force it exerts to pull itself back to its relaxed shape—called a restoring force —as a standard. The magnitude of all other forces can be stated as multiples of this standard unit of force. Many other possibilities exist for standard forces. (One that we will encounter in Magnetism is the magnetic force between two wires carrying electric current.) Some alternative definitions of force will be given later in this chapter.
To investigate force standards and cause and effect, get two identical rubber bands. Hang one rubber band vertically on a hook. Find a small household item that could be attached to the rubber band using a paper clip, and use this item as a weight to investigate the stretch of the rubber band. Measure the amount of stretch produced in the rubber band with one, two, and four of these (identical) items suspended from the rubber band. What is the relationship between the number of items and the amount of stretch? How large a stretch would you expect for the same number of items suspended from two rubber bands? What happens to the amount of stretch of the rubber band (with the weights attached) if the weights are also pushed to the side with a pencil?
Propose a force standard different from the example of a stretched spring discussed in the text. Your standard must be capable of producing the same force repeatedly.
What properties do forces have that allow us to classify them as vectors?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?