| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The magnetic field lines also propagate away from the antenna at the speed of light, forming the other part of the electromagnetic wave, as seen in [link] (b). The magnetic part of the wave has the same period and wavelength as the electric part, since they are both produced by the same movement and separation of charges in the antenna.
The electric and magnetic waves are shown together at one instant in time in [link] . The electric and magnetic fields produced by a long straight wire antenna are exactly in phase. Note that they are perpendicular to one another and to the direction of propagation, making this a transverse wave .
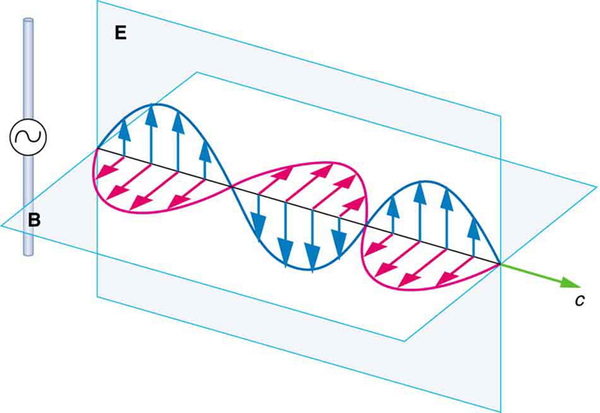
Electromagnetic waves generally propagate out from a source in all directions, sometimes forming a complex radiation pattern. A linear antenna like this one will not radiate parallel to its length, for example. The wave is shown in one direction from the antenna in [link] to illustrate its basic characteristics.
Instead of the AC generator, the antenna can also be driven by an AC circuit. In fact, charges radiate whenever they are accelerated. But while a current in a circuit needs a complete path, an antenna has a varying charge distribution forming a standing wave , driven by the AC. The dimensions of the antenna are critical for determining the frequency of the radiated electromagnetic waves. This is a resonant phenomenon and when we tune radios or TV, we vary electrical properties to achieve appropriate resonant conditions in the antenna.
Electromagnetic waves carry energy away from their source, similar to a sound wave carrying energy away from a standing wave on a guitar string. An antenna for receiving EM signals works in reverse. And like antennas that produce EM waves, receiver antennas are specially designed to resonate at particular frequencies.
An incoming electromagnetic wave accelerates electrons in the antenna, setting up a standing wave. If the radio or TV is switched on, electrical components pick up and amplify the signal formed by the accelerating electrons. The signal is then converted to audio and/or video format. Sometimes big receiver dishes are used to focus the signal onto an antenna.
In fact, charges radiate whenever they are accelerated. When designing circuits, we often assume that energy does not quickly escape AC circuits, and mostly this is true. A broadcast antenna is specially designed to enhance the rate of electromagnetic radiation, and shielding is necessary to keep the radiation close to zero. Some familiar phenomena are based on the production of electromagnetic waves by varying currents. Your microwave oven, for example, sends electromagnetic waves, called microwaves, from a concealed antenna that has an oscillating current imposed on it.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?