| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Power is the rate at which work is done or energy in any form is used or supplied. To see the relationship of power to fluid flow, consider Bernoulli’s equation:
All three terms have units of energy per unit volume, as discussed in the previous section. Now, considering units, if we multiply energy per unit volume by flow rate (volume per unit time), we get units of power. That is, . This means that if we multiply Bernoulli’s equation by flow rate , we get power. In equation form, this is
Each term has a clear physical meaning. For example, is the power supplied to a fluid, perhaps by a pump, to give it its pressure . Similarly, is the power supplied to a fluid to give it its kinetic energy. And is the power going to gravitational potential energy.
Power is defined as the rate of energy transferred, or . Fluid flow involves several types of power. Each type of power is identified with a specific type of energy being expended or changed in form.
Suppose the fire hose in the previous example is fed by a pump that receives water through a hose with a 6.40-cm diameter coming from a hydrant with a pressure of . What power does the pump supply to the water?
Strategy
Here we must consider energy forms as well as how they relate to fluid flow. Since the input and output hoses have the same diameters and are at the same height, the pump does not change the speed of the water nor its height, and so the water’s kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy are unchanged. That means the pump only supplies power to increase water pressure by (from to ).
Solution
As discussed above, the power associated with pressure is
Discussion
Such a substantial amount of power requires a large pump, such as is found on some fire trucks. (This kilowatt value converts to about 50 hp.) The pump in this example increases only the water’s pressure. If a pump—such as the heart—directly increases velocity and height as well as pressure, we would have to calculate all three terms to find the power it supplies.
Based on Bernoulli’s equation, what are three forms of energy in a fluid? (Note that these forms are conservative, unlike heat transfer and other dissipative forms not included in Bernoulli’s equation.)
Water that has emerged from a hose into the atmosphere has a gauge pressure of zero. Why? When you put your hand in front of the emerging stream you feel a force, yet the water’s gauge pressure is zero. Explain where the force comes from in terms of energy.
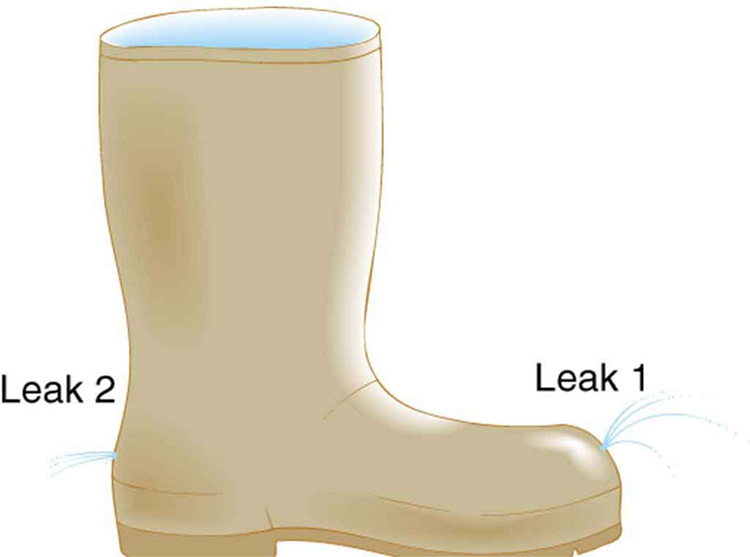
The old rubber boot shown in [link] has two leaks. To what maximum height can the water squirt from Leak 1? How does the velocity of water emerging from Leak 2 differ from that of leak 1? Explain your responses in terms of energy.
Water pressure inside a hose nozzle can be less than atmospheric pressure due to the Bernoulli effect. Explain in terms of energy how the water can emerge from the nozzle against the opposing atmospheric pressure.
Hoover Dam on the Colorado River is the highest dam in the United States at 221 m, with an output of 1300 MW. The dam generates electricity with water taken from a depth of 150 m and an average flow rate of . (a) Calculate the power in this flow. (b) What is the ratio of this power to the facility’s average of 680 MW?
(a)
(b) 1.4
A frequently quoted rule of thumb in aircraft design is that wings should produce about 1000 N of lift per square meter of wing. (The fact that a wing has a top and bottom surface does not double its area.) (a) At takeoff, an aircraft travels at 60.0 m/s, so that the air speed relative to the bottom of the wing is 60.0 m/s. Given the sea level density of air to be , how fast must it move over the upper surface to create the ideal lift? (b) How fast must air move over the upper surface at a cruising speed of 245 m/s and at an altitude where air density is one-fourth that at sea level? (Note that this is not all of the aircraft’s lift—some comes from the body of the plane, some from engine thrust, and so on. Furthermore, Bernoulli’s principle gives an approximate answer because flow over the wing creates turbulence.)
The left ventricle of a resting adult’s heart pumps blood at a flow rate of , increasing its pressure by 110 mm Hg, its speed from zero to 30.0 cm/s, and its height by 5.00 cm. (All numbers are averaged over the entire heartbeat.) Calculate the total power output of the left ventricle. Note that most of the power is used to increase blood pressure.
1.26 W
A sump pump (used to drain water from the basement of houses built below the water table) is draining a flooded basement at the rate of 0.750 L/s, with an output pressure of . (a) The water enters a hose with a 3.00-cm inside diameter and rises 2.50 m above the pump. What is its pressure at this point? (b) The hose goes over the foundation wall, losing 0.500 m in height, and widens to 4.00 cm in diameter. What is the pressure now? You may neglect frictional losses in both parts of the problem.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?