| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
(a) Using the symmetry of the arrangement, show that the electric field at the center of the square in [link] is zero if the charges on the four corners are exactly equal. (b) Show that this is also true for any combination of charges in which and
(a) What is the direction of the total Coulomb force on in [link] if is negative, and both are negative, and and both are positive? (b) What is the direction of the electric field at the center of the square in this situation?
Considering [link] , suppose that and . First show that is in static equilibrium. (You may neglect the gravitational force.) Then discuss whether the equilibrium is stable or unstable, noting that this may depend on the signs of the charges and the direction of displacement of from the center of the square.
If in [link] , under what conditions will there be no net Coulomb force on ?
In regions of low humidity, one develops a special “grip” when opening car doors, or touching metal door knobs. This involves placing as much of the hand on the device as possible, not just the ends of one’s fingers. Discuss the induced charge and explain why this is done.
Tollbooth stations on roadways and bridges usually have a piece of wire stuck in the pavement before them that will touch a car as it approaches. Why is this done?
Suppose a woman carries an excess charge. To maintain her charged status can she be standing on ground wearing just any pair of shoes? How would you discharge her? What are the consequences if she simply walks away?
Sketch the electric field lines in the vicinity of the conductor in [link] given the field was originally uniform and parallel to the object’s long axis. Is the resulting field small near the long side of the object?

Sketch the electric field lines in the vicinity of the conductor in [link] given the field was originally uniform and parallel to the object’s long axis. Is the resulting field small near the long side of the object?

Sketch the electric field between the two conducting plates shown in [link] , given the top plate is positive and an equal amount of negative charge is on the bottom plate. Be certain to indicate the distribution of charge on the plates.
Sketch the electric field lines in the vicinity of the charged insulator in [link] noting its nonuniform charge distribution.
What is the force on the charge located at in [link] (a) given that ?
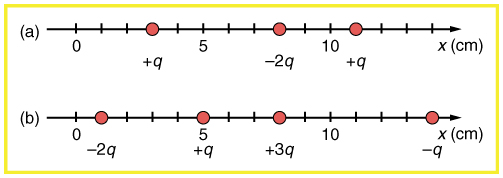
(a) Find the total electric field at in [link] (b) given that . (b) Find the total electric field at in [link] (b). (c) If the charges are allowed to move and eventually be brought to rest by friction, what will the final charge configuration be? (That is, will there be a single charge, double charge, etc., and what will its value(s) be?)
(a)
(b)
(c) one charge of
(a) Find the electric field at in [link] (a), given that . (b) At what position between 3.00 and 8.00 cm is the total electric field the same as that for alone? (c) Can the electric field be zero anywhere between 0.00 and 8.00 cm? (d) At very large positive or negative values of x , the electric field approaches zero in both (a) and (b). In which does it most rapidly approach zero and why? (e) At what position to the right of 11.0 cm is the total electric field zero, other than at infinity? (Hint: A graphing calculator can yield considerable insight in this problem.)
(a) Find the total Coulomb force on a charge of 2.00 nC located at in [link] (b), given that . (b) Find the x -position at which the electric field is zero in [link] (b).
(a) 0.252 N to the left
(b)
Using the symmetry of the arrangement, determine the direction of the force on in the figure below, given that and . (b) Calculate the magnitude of the force on the charge , given that the square is 10.0 cm on a side and .
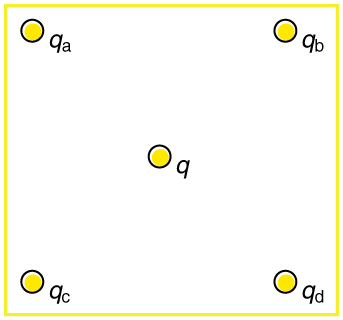
(a) Using the symmetry of the arrangement, determine the direction of the electric field at the center of the square in [link] , given that and . (b) Calculate the magnitude of the electric field at the location of , given that the square is 5.00 cm on a side.
(a)The electric field at the center of the square will be straight up, since and are positive and and are negative and all have the same magnitude.
(b)
Find the electric field at the location of in [link] given that , , and the square is 20.0 cm on a side.
Find the total Coulomb force on the charge in [link] , given that , , , , and . The square is 50.0 cm on a side.
in the direction
(a) Find the electric field at the location of in [link] , given that and . (b) What is the force on , given that ?
(a) Find the electric field at the center of the triangular configuration of charges in [link] , given that , , and . (b) Is there any combination of charges, other than , that will produce a zero strength electric field at the center of the triangular configuration?
(a) , below the horizontal.
(b) No

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?