| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
| Substance | Critical temperature | Critical pressure | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 647.4 | 374.3 | 219.0 | |
| Sulfur dioxide | 430.7 | 157.6 | 78.0 | |
| Ammonia | 405.5 | 132.4 | 111.7 | |
| Carbon dioxide | 304.2 | 31.1 | 73.2 | |
| Oxygen | 154.8 | −118.4 | 50.3 | |
| Nitrogen | 126.2 | −146.9 | 33.6 | |
| Hydrogen | 33.3 | −239.9 | 12.9 | |
| Helium | 5.3 | −267.9 | 2.27 |
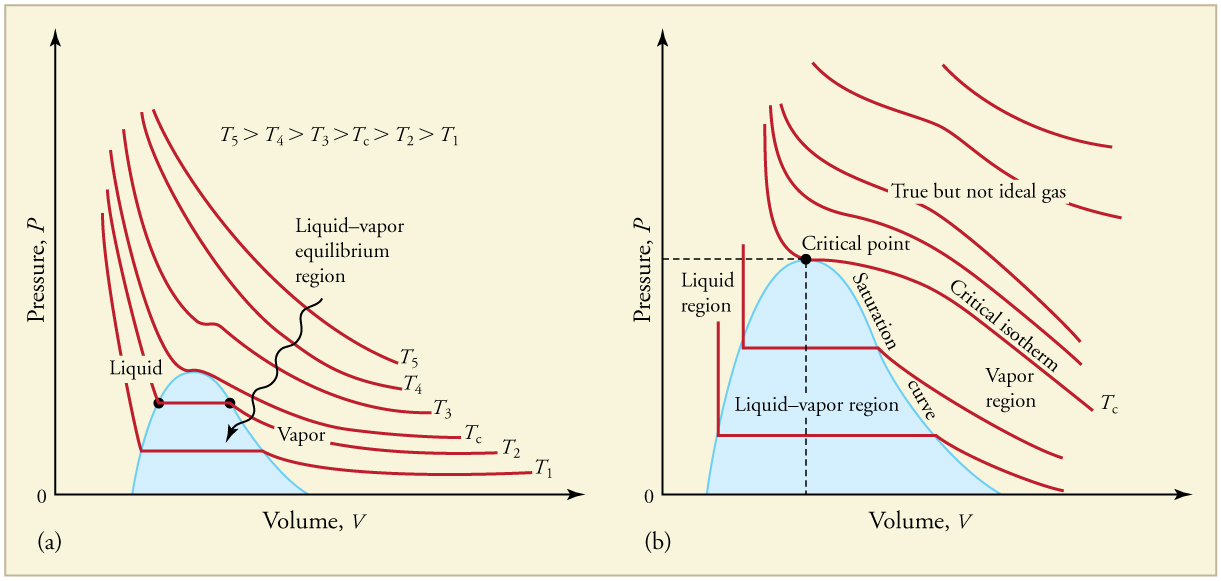
The plots of pressure versus temperatures provide considerable insight into thermal properties of substances. There are well-defined regions on these graphs that correspond to various phases of matter, so graphs are called phase diagrams . [link] shows the phase diagram for water. Using the graph, if you know the pressure and temperature you can determine the phase of water. The solid lines—boundaries between phases—indicate temperatures and pressures at which the phases coexist (that is, they exist together in ratios, depending on pressure and temperature). For example, the boiling point of water is at 1.00 atm. As the pressure increases, the boiling temperature rises steadily to at a pressure of 218 atm. A pressure cooker (or even a covered pot) will cook food faster because the water can exist as a liquid at temperatures greater than without all boiling away. The curve ends at a point called the critical point , because at higher temperatures the liquid phase does not exist at any pressure. The critical point occurs at the critical temperature, as you can see for water from [link] . The critical temperature for oxygen is , so oxygen cannot be liquefied above this temperature.
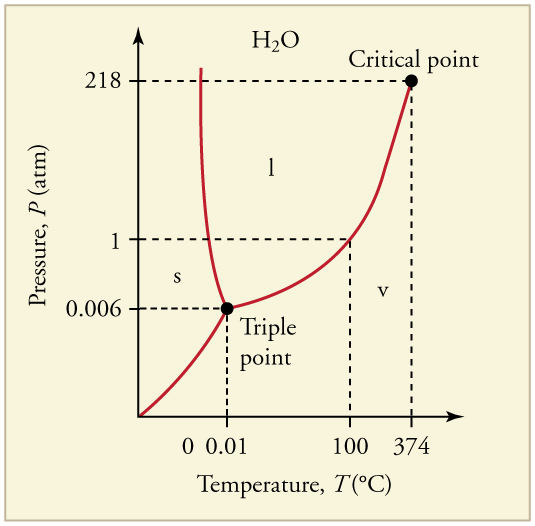
Similarly, the curve between the solid and liquid regions in [link] gives the melting temperature at various pressures. For example, the melting point is at 1.00 atm, as expected. Note that, at a fixed temperature, you can change the phase from solid (ice) to liquid (water) by increasing the pressure. Ice melts from pressure in the hands of a snowball maker. From the phase diagram, we can also say that the melting temperature of ice rises with increased pressure. When a car is driven over snow, the increased pressure from the tires melts the snowflakes; afterwards the water refreezes and forms an ice layer.
At sufficiently low pressures there is no liquid phase, but the substance can exist as either gas or solid. For water, there is no liquid phase at pressures below 0.00600 atm. The phase change from solid to gas is called sublimation . It accounts for large losses of snow pack that never make it into a river, the routine automatic defrosting of a freezer, and the freeze-drying process applied to many foods. Carbon dioxide, on the other hand, sublimates at standard atmospheric pressure of 1 atm. (The solid form of is known as dry ice because it does not melt. Instead, it moves directly from the solid to the gas state.)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?