| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Strategy
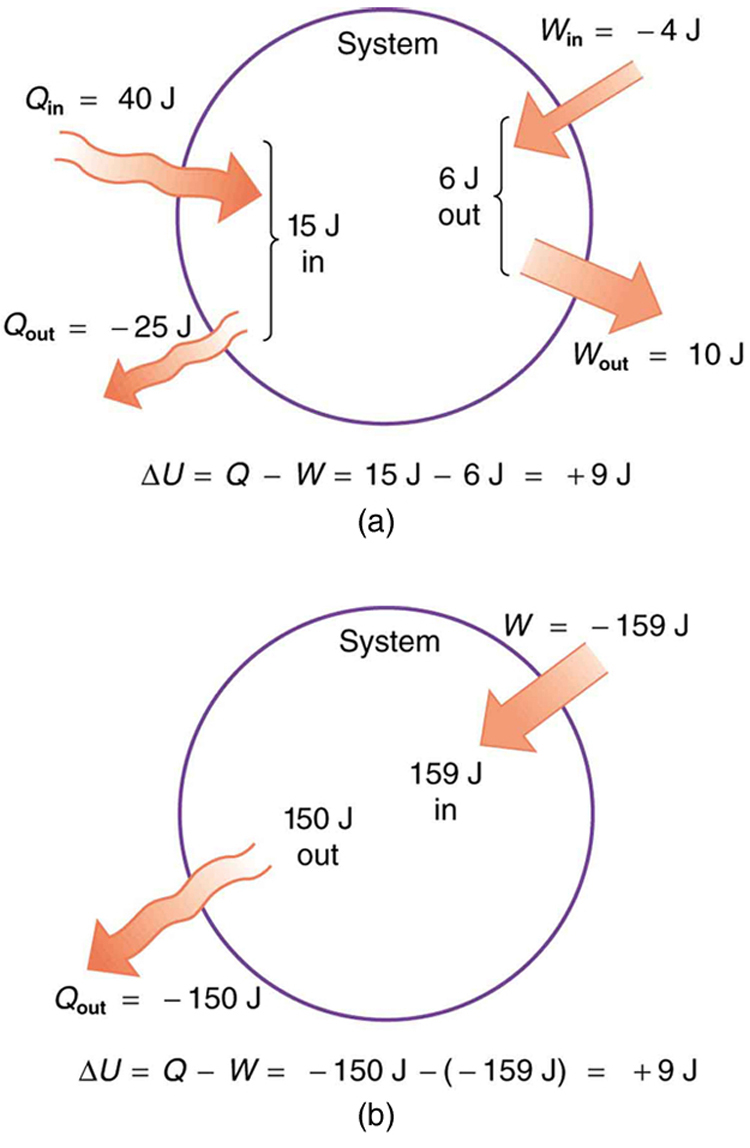
In part (a), we must first find the net heat transfer and net work done from the given information. Then the first law of thermodynamics can be used to find the change in internal energy. In part (b), the net heat transfer and work done are given, so the equation can be used directly.
Solution for (a)
The net heat transfer is the heat transfer into the system minus the heat transfer out of the system, or
Similarly, the total work is the work done by the system minus the work done on the system, or
Thus the change in internal energy is given by the first law of thermodynamics:
We can also find the change in internal energy for each of the two steps. First, consider 40.00 J of heat transfer in and 10.00 J of work out, or
Now consider 25.00 J of heat transfer out and 4.00 J of work in, or
The total change is the sum of these two steps, or
Discussion on (a)
No matter whether you look at the overall process or break it into steps, the change in internal energy is the same.
Solution for (b)
Here the net heat transfer and total work are given directly to be and , so that
Discussion on (b)
A very different process in part (b) produces the same 9.00-J change in internal energy as in part (a). Note that the change in the system in both parts is related to and not to the individual s or s involved. The system ends up in the same state in both (a) and (b). Parts (a) and (b) present two different paths for the system to follow between the same starting and ending points, and the change in internal energy for each is the same—it is independent of path.
Human metabolism is the conversion of food into heat transfer, work, and stored fat. Metabolism is an interesting example of the first law of thermodynamics in action. We now take another look at these topics via the first law of thermodynamics. Considering the body as the system of interest, we can use the first law to examine heat transfer, doing work, and internal energy in activities ranging from sleep to heavy exercise. What are some of the major characteristics of heat transfer, doing work, and energy in the body? For one, body temperature is normally kept constant by heat transfer to the surroundings. This means is negative. Another fact is that the body usually does work on the outside world. This means is positive. In such situations, then, the body loses internal energy, since is negative.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?