| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The circulatory system provides many examples of Poiseuille’s law in action—with blood flow regulated by changes in vessel size and blood pressure. Blood vessels are not rigid but elastic. Adjustments to blood flow are primarily made by varying the size of the vessels, since the resistance is so sensitive to the radius. During vigorous exercise, blood vessels are selectively dilated to important muscles and organs and blood pressure increases. This creates both greater overall blood flow and increased flow to specific areas. Conversely, decreases in vessel radii, perhaps from plaques in the arteries, can greatly reduce blood flow. If a vessel’s radius is reduced by only 5% (to 0.95 of its original value), the flow rate is reduced to about of its original value. A 19% decrease in flow is caused by a 5% decrease in radius. The body may compensate by increasing blood pressure by 19%, but this presents hazards to the heart and any vessel that has weakened walls. Another example comes from automobile engine oil. If you have a car with an oil pressure gauge, you may notice that oil pressure is high when the engine is cold. Motor oil has greater viscosity when cold than when warm, and so pressure must be greater to pump the same amount of cold oil.
An intravenous (IV) system is supplying saline solution to a patient at the rate of through a needle of radius 0.150 mm and length 2.50 cm. What pressure is needed at the entrance of the needle to cause this flow, assuming the viscosity of the saline solution to be the same as that of water? The gauge pressure of the blood in the patient’s vein is 8.00 mm Hg. (Assume that the temperature is .)
Strategy
Assuming laminar flow, Poiseuille’s law applies. This is given by
where is the pressure at the entrance of the needle and is the pressure in the vein. The only unknown is .
Solution
Solving for yields
is given as 8.00 mm Hg, which converts to . Substituting this and the other known values yields
Discussion
This pressure could be supplied by an IV bottle with the surface of the saline solution 1.61 m above the entrance to the needle (this is left for you to solve in this chapter’s Problems and Exercises), assuming that there is negligible pressure drop in the tubing leading to the needle.
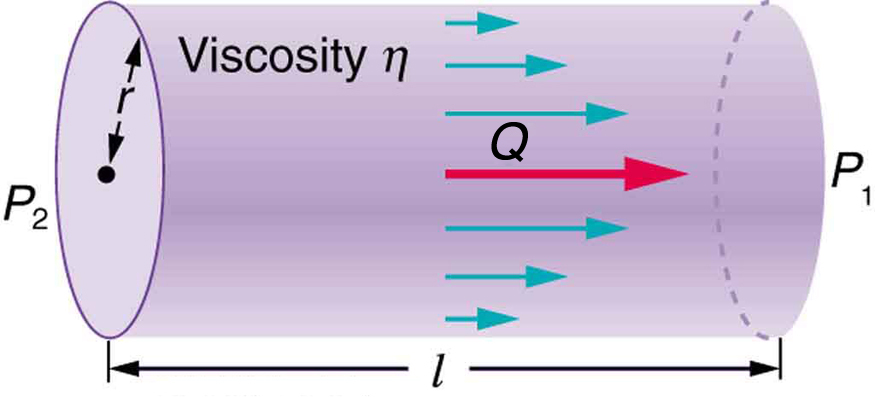
You may have noticed that water pressure in your home might be lower than normal on hot summer days when there is more use. This pressure drop occurs in the water main before it reaches your home. Let us consider flow through the water main as illustrated in [link] . We can understand why the pressure to the home drops during times of heavy use by rearranging

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?