| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The image in which light rays from one point on the object actually cross at the location of the image and can be projected onto a screen, a piece of film, or the retina of an eye is called a real image.
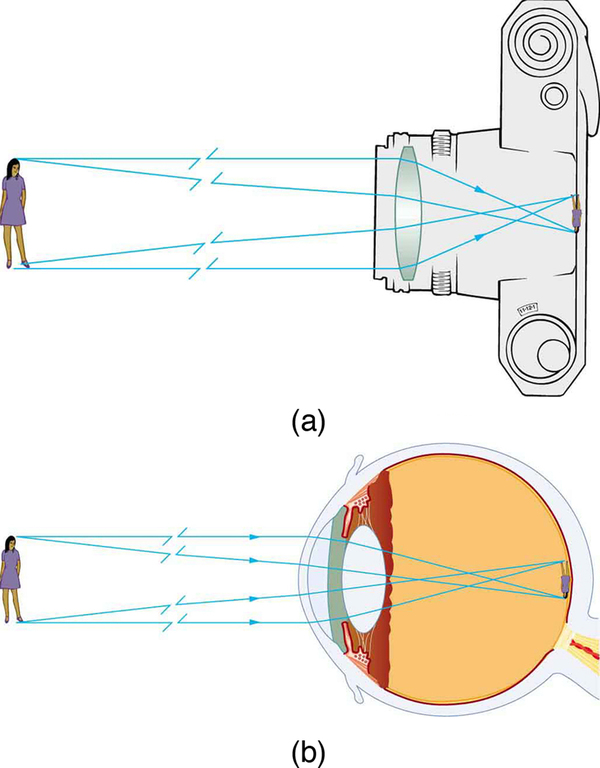
Several important distances appear in [link] . We define to be the object distance, the distance of an object from the center of a lens. Image distance is defined to be the distance of the image from the center of a lens. The height of the object and height of the image are given the symbols and , respectively. Images that appear upright relative to the object have heights that are positive and those that are inverted have negative heights. Using the rules of ray tracing and making a scale drawing with paper and pencil, like that in [link] , we can accurately describe the location and size of an image. But the real benefit of ray tracing is in visualizing how images are formed in a variety of situations. To obtain numerical information, we use a pair of equations that can be derived from a geometric analysis of ray tracing for thin lenses. The thin lens equations are
and
We define the ratio of image height to object height ( ) to be the magnification . (The minus sign in the equation above will be discussed shortly.) The thin lens equations are broadly applicable to all situations involving thin lenses (and “thin” mirrors, as we will see later). We will explore many features of image formation in the following worked examples.
The distance of the image from the center of the lens is called image distance.
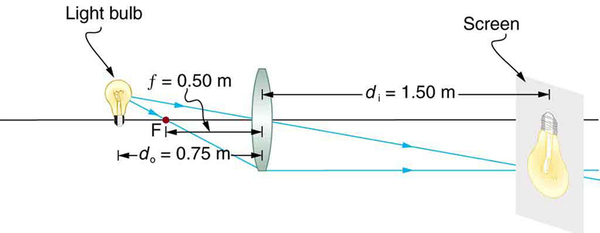
A clear glass light bulb is placed 0.750 m from a convex lens having a 0.500 m focal length, as shown in [link] . Use ray tracing to get an approximate location for the image. Then use the thin lens equations to calculate (a) the location of the image and (b) its magnification. Verify that ray tracing and the thin lens equations produce consistent results.
Strategy and Concept
Since the object is placed farther away from a converging lens than the focal length of the lens, this situation is analogous to those illustrated in [link] and [link] . Ray tracing to scale should produce similar results for . Numerical solutions for and can be obtained using the thin lens equations, noting that .
Solutions (Ray tracing)
The ray tracing to scale in [link] shows two rays from a point on the bulb’s filament crossing about 1.50 m on the far side of the lens. Thus the image distance is about 1.50 m. Similarly, the image height based on ray tracing is greater than the object height by about a factor of 2, and the image is inverted. Thus is about –2. The minus sign indicates that the image is inverted.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?