| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Voltage on the capacitor is initially zero and rises rapidly at first, since the initial current is a maximum. [link] (b) shows a graph of capacitor voltage versus time ( ) starting when the switch is closed at . The voltage approaches emf asymptotically, since the closer it gets to emf the less current flows. The equation for voltage versus time when charging a capacitor through a resistor , derived using calculus, is
where is the voltage across the capacitor, emf is equal to the emf of the DC voltage source, and the exponential e = 2.718 … is the base of the natural logarithm. Note that the units of are seconds. We define
where (the Greek letter tau) is called the time constant for an circuit. As noted before, a small resistance allows the capacitor to charge faster. This is reasonable, since a larger current flows through a smaller resistance. It is also reasonable that the smaller the capacitor , the less time needed to charge it. Both factors are contained in .
More quantitatively, consider what happens when . Then the voltage on the capacitor is
This means that in the time , the voltage rises to 0.632 of its final value. The voltage will rise 0.632 of the remainder in the next time . It is a characteristic of the exponential function that the final value is never reached, but 0.632 of the remainder to that value is achieved in every time, . In just a few multiples of the time constant , then, the final value is very nearly achieved, as the graph in [link] (b) illustrates.
Discharging a capacitor through a resistor proceeds in a similar fashion, as [link] illustrates. Initially, the current is , driven by the initial voltage on the capacitor. As the voltage decreases, the current and hence the rate of discharge decreases, implying another exponential formula for . Using calculus, the voltage on a capacitor being discharged through a resistor is found to be
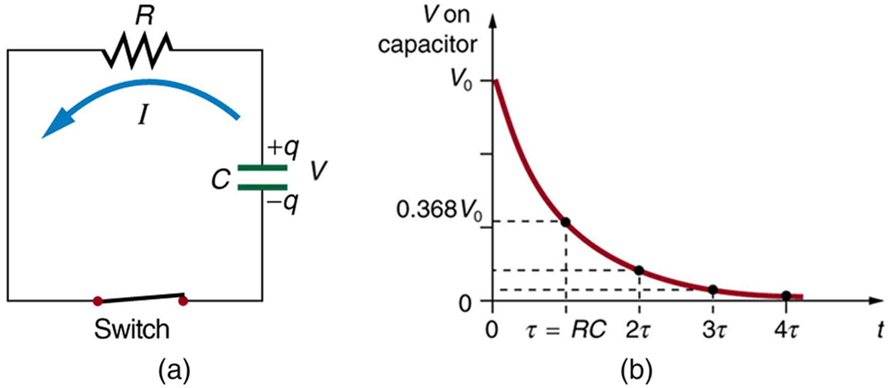
The graph in [link] (b) is an example of this exponential decay. Again, the time constant is . A small resistance allows the capacitor to discharge in a small time, since the current is larger. Similarly, a small capacitance requires less time to discharge, since less charge is stored. In the first time interval after the switch is closed, the voltage falls to 0.368 of its initial value, since .
During each successive time , the voltage falls to 0.368 of its preceding value. In a few multiples of , the voltage becomes very close to zero, as indicated by the graph in [link] (b).
Now we can explain why the flash camera in our scenario takes so much longer to charge than discharge; the resistance while charging is significantly greater than while discharging. The internal resistance of the battery accounts for most of the resistance while charging. As the battery ages, the increasing internal resistance makes the charging process even slower. (You may have noticed this.)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?