| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Electrostatic repulsion in the leaves of the charged electroscope separates them. The electrostatic force has a horizontal component that results in the leaves moving apart as well as a vertical component that is balanced by the gravitational force. Similarly, the electroscope can be negatively charged by contact with a negatively charged object.
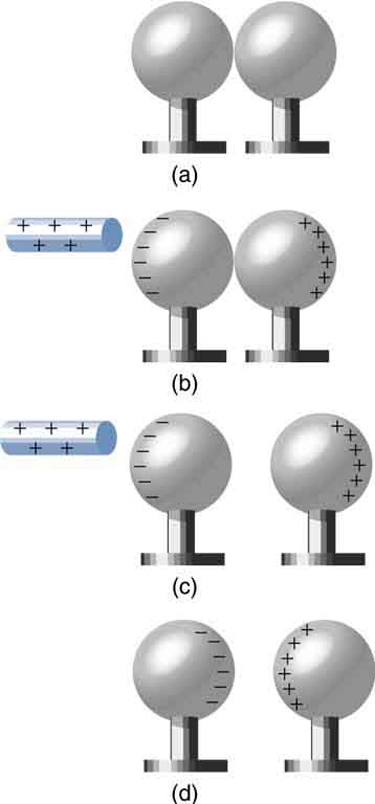
It is not necessary to transfer excess charge directly to an object in order to charge it. [link] shows a method of induction wherein a charge is created in a nearby object, without direct contact. Here we see two neutral metal spheres in contact with one another but insulated from the rest of the world. A positively charged rod is brought near one of them, attracting negative charge to that side, leaving the other sphere positively charged.
This is an example of induced polarization of neutral objects. Polarization is the separation of charges in an object that remains neutral. If the spheres are now separated (before the rod is pulled away), each sphere will have a net charge. Note that the object closest to the charged rod receives an opposite charge when charged by induction. Note also that no charge is removed from the charged rod, so that this process can be repeated without depleting the supply of excess charge.
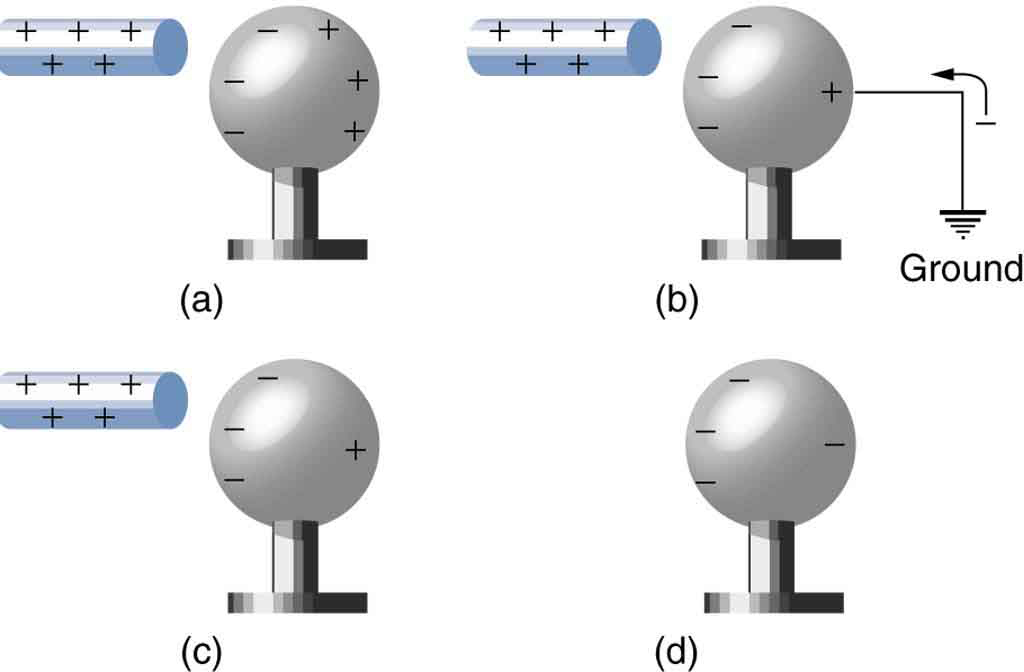
Another method of charging by induction is shown in [link] . The neutral metal sphere is polarized when a charged rod is brought near it. The sphere is then grounded, meaning that a conducting wire is run from the sphere to the ground. Since the earth is large and most ground is a good conductor, it can supply or accept excess charge easily. In this case, electrons are attracted to the sphere through a wire called the ground wire, because it supplies a conducting path to the ground. The ground connection is broken before the charged rod is removed, leaving the sphere with an excess charge opposite to that of the rod. Again, an opposite charge is achieved when charging by induction and the charged rod loses none of its excess charge.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?