| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
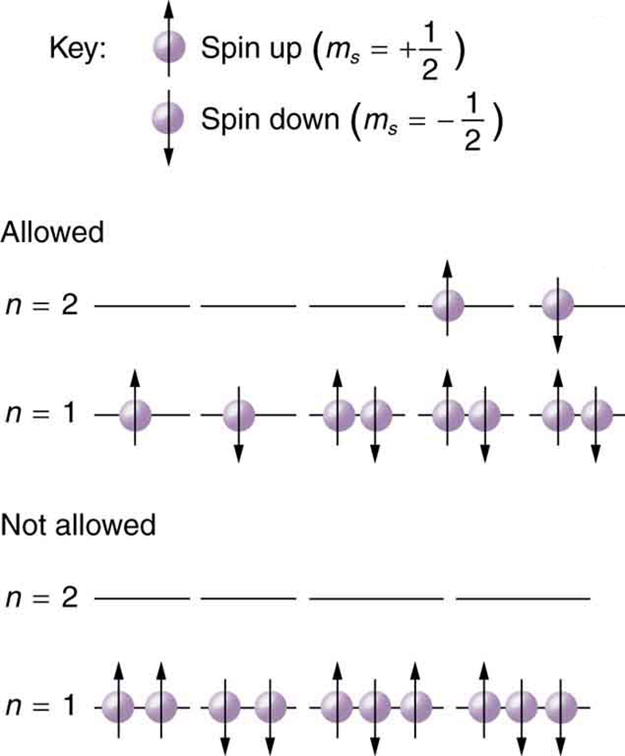
Because of the Pauli exclusion principle, only hydrogen and helium can have all of their electrons in the state. Lithium (see the periodic table) has three electrons, and so one must be in the level. This leads to the concept of shells and shell filling. As we progress up in the number of electrons, we go from hydrogen to helium, lithium, beryllium, boron, and so on, and we see that there are limits to the number of electrons for each value of . Higher values of the shell correspond to higher energies, and they can allow more electrons because of the various combinations of , and that are possible. Each value of the principal quantum number thus corresponds to an atomic shell into which a limited number of electrons can go. Shells and the number of electrons in them determine the physical and chemical properties of atoms, since it is the outermost electrons that interact most with anything outside the atom.
The probability clouds of electrons with the lowest value of are closest to the nucleus and, thus, more tightly bound. Thus when shells fill, they start with , progress to , and so on. Each value of thus corresponds to a subshell .
The table given below lists symbols traditionally used to denote shells and subshells.
| Shell | Subshell | |
|---|---|---|
| Symbol | ||
| 1 | 0 | |
| 2 | 1 | |
| 3 | 2 | |
| 4 | 3 | |
| 5 | 4 | |
| 5 | ||
| 6 It is unusual to deal with subshells having greater than 6, but when encountered, they continue to be labeled in alphabetical order. |
To denote shells and subshells, we write with a number for and a letter for . For example, an electron in the state must have , and it is denoted as a electron. Two electrons in the state is denoted as . Another example is an electron in the state with , written as . The case of three electrons with these quantum numbers is written . This notation, called spectroscopic notation, is generalized as shown in [link] .
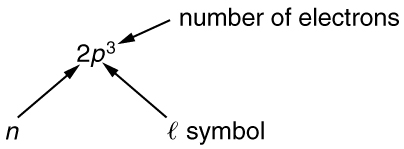
Counting the number of possible combinations of quantum numbers allowed by the exclusion principle, we can determine how many electrons it takes to fill each subshell and shell.
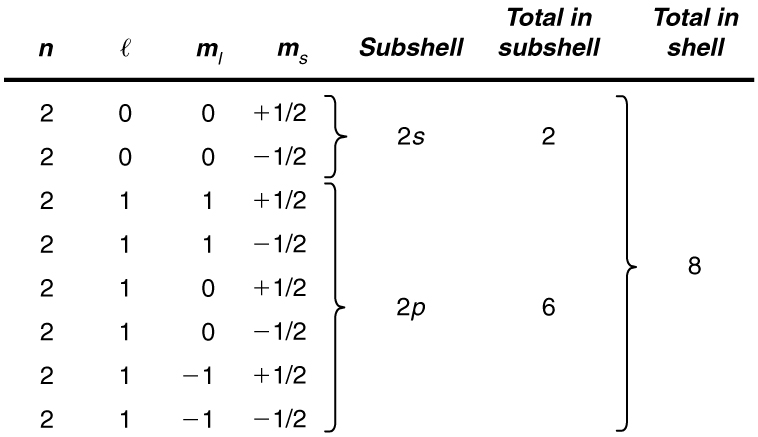
List all the possible sets of quantum numbers for the shell, and determine the number of electrons that can be in the shell and each of its subshells.
Strategy
Given for the shell, the rules for quantum numbers limit to be 0 or 1. The shell therefore has two subshells, labeled and . Since the lowest subshell fills first, we start with the subshell possibilities and then proceed with the subshell.
Solution
It is convenient to list the possible quantum numbers in a table, as shown below.
Discussion
It is laborious to make a table like this every time we want to know how many electrons can be in a shell or subshell. There exist general rules that are easy to apply, as we shall now see.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?