| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
If a person rows a boat across a rapidly flowing river and tries to head directly for the other shore, the boat instead moves diagonally relative to the shore, as in [link] . The boat does not move in the direction in which it is pointed. The reason, of course, is that the river carries the boat downstream. Similarly, if a small airplane flies overhead in a strong crosswind, you can sometimes see that the plane is not moving in the direction in which it is pointed, as illustrated in [link] . The plane is moving straight ahead relative to the air, but the movement of the air mass relative to the ground carries it sideways.
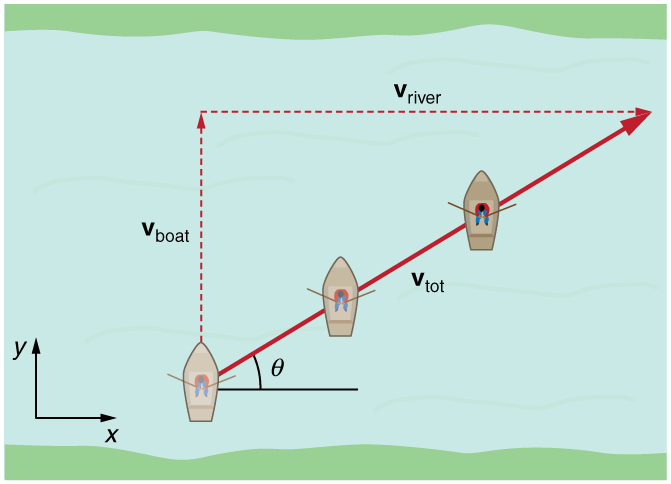
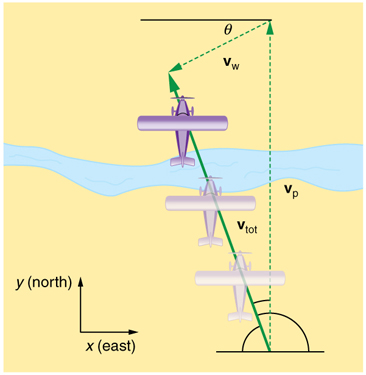
In each of these situations, an object has a velocity relative to a medium (such as a river) and that medium has a velocity relative to an observer on solid ground. The velocity of the object relative to the observer is the sum of these velocity vectors, as indicated in [link] and [link] . These situations are only two of many in which it is useful to add velocities. In this module, we first re-examine how to add velocities and then consider certain aspects of what relative velocity means.
How do we add velocities? Velocity is a vector (it has both magnitude and direction); the rules of vector addition discussed in Vector Addition and Subtraction: Graphical Methods and Vector Addition and Subtraction: Analytical Methods apply to the addition of velocities, just as they do for any other vectors. In one-dimensional motion, the addition of velocities is simple—they add like ordinary numbers. For example, if a field hockey player is moving at straight toward the goal and drives the ball in the same direction with a velocity of relative to her body, then the velocity of the ball is relative to the stationary, profusely sweating goalkeeper standing in front of the goal.
In two-dimensional motion, either graphical or analytical techniques can be used to add velocities. We will concentrate on analytical techniques. The following equations give the relationships between the magnitude and direction of velocity ( and ) and its components ( and ) along the x - and y -axes of an appropriately chosen coordinate system:
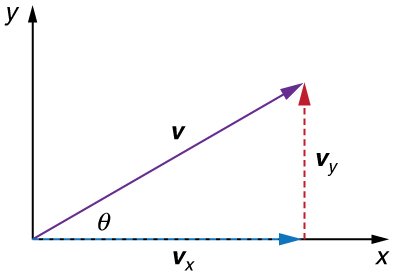
These equations are valid for any vectors and are adapted specifically for velocity. The first two equations are used to find the components of a velocity when its magnitude and direction are known. The last two are used to find the magnitude and direction of velocity when its components are known.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?