| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

Your feet feel cold as you walk barefoot across the living room carpet in your cold house and then step onto the kitchen tile floor. This result is intriguing, since the carpet and tile floor are both at the same temperature. The different sensation you feel is explained by the different rates of heat transfer: the heat loss during the same time interval is greater for skin in contact with the tiles than with the carpet, so the temperature drop is greater on the tiles.
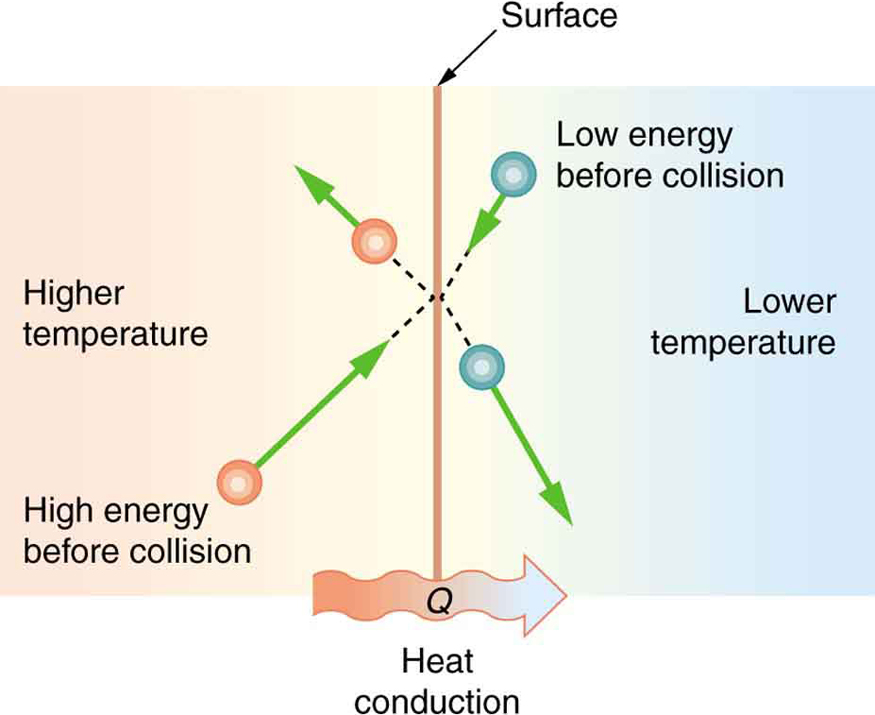
Some materials conduct thermal energy faster than others. In general, good conductors of electricity (metals like copper, aluminum, gold, and silver) are also good heat conductors, whereas insulators of electricity (wood, plastic, and rubber) are poor heat conductors. [link] shows molecules in two bodies at different temperatures. The (average) kinetic energy of a molecule in the hot body is higher than in the colder body. If two molecules collide, an energy transfer from the molecule with greater kinetic energy to the molecule with less kinetic energy occurs. The cumulative effect from all collisions results in a net flux of heat from the hot body to the colder body. The heat flux thus depends on the temperature difference . Therefore, you will get a more severe burn from boiling water than from hot tap water. Conversely, if the temperatures are the same, the net heat transfer rate falls to zero, and equilibrium is achieved. Owing to the fact that the number of collisions increases with increasing area, heat conduction depends on the cross-sectional area. If you touch a cold wall with your palm, your hand cools faster than if you just touch it with your fingertip.
A third factor in the mechanism of conduction is the thickness of the material through which heat transfers. The figure below shows a slab of material with different temperatures on either side. Suppose that is greater than , so that heat is transferred from left to right. Heat transfer from the left side to the right side is accomplished by a series of molecular collisions. The thicker the material, the more time it takes to transfer the same amount of heat. This model explains why thick clothing is warmer than thin clothing in winters, and why Arctic mammals protect themselves with thick blubber.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?