| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
It has been pointed out that any motion, that changes directions, requires more than one dimension for representation. Circular motion by the geometry of the trajectory is two dimensional motion.
In the case of circular motion, it is a matter of convenience to locate origin of the two dimensional coordinate system at the center of circle. This choice ensures the symmetry of the circular motion about the origin of the reference system.
The coordinates of the particle is given by the "x" and "y" coordinate pair as :
The angle "θ" is measured anti-clockwise from x-axis.
The position vector of the position of the particle, r , is represented in terms of unit vectors as :
The magnitude of velocity of the particle (v) is constant by the definition of uniform circular motion. In component form, the velocity (refer to the figure) is :
From the geometry as shown in the figure,
Uniform circular motion
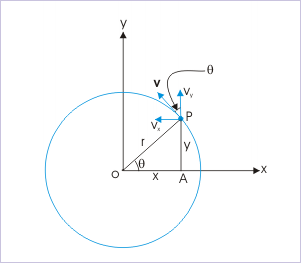
We may emphasize here that it is always easy to find the sign of the component of a vector like velocity. Decide the sign by the direction of component (projection) with respect to positive direction of reference axis. Note from the figure that component along x-direction is opposite to the positive reference direction and hence negative.
From the ΔOAP,
Putting these values in the expression for velocity, we have :
We are now sufficiently equipped and familiarized with the nature of uniform circular motion and the associated centripetal (center seeking) acceleration. Now, we seek to determine this acceleration.
Knowing that speed, "v" and radius of circle, "r" are constants, we differentiate the expression of velocity with respect to time to obtain expression for centripetal acceleration as :
Putting values of component velocities in terms of angle,
Uniform circular motion

where
It is evident from the equation of acceleration that it varies as the angle with horizontal, "θ" changes. The magnitude of acceleration is :
The radius of the circle is constant. The magnitude of velocity i.e. speed, "v" is constant for UCM. It, then, follows that though velocity changes with the motion (angle from reference direction), but the speed of the particle in UCM is a constant.
Problem : A cyclist negotiates the curvature of 20 m with a speed of 20 m/s. What is the magnitude of his acceleration?
Solution : The speed of the cyclist is constant. The acceleration of cyclist, therefore, is the centripetal acceleration required to move the cyclist along a circular path i.e. the acceleration resulting from the change in the direction of motion along the circular path.
Here, v = 20 m/s and r = 20 m

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for k-12' conversation and receive update notifications?