| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We are required to find minimum force. We need to understand the implication of this phrase. It is clear that we can apply external force in such a manner that block of “2 kg” acquires kinetic energy by the time block of “1 kg” is initiated in motion. Alternatively as a base case, we can apply external force gradually and slowly in increasing magnitude till the block of “1 kg” is initiated in motion. In this case, the block of “2 kg” does not acquire kinetic energy. This mode of application of external force represents the situation when minimum external force will be required to initiate block of “1 kg”. Hence,
Motion of block is constrained in horizontal direction. There is no change of vertical elevation. Hence, there is no change in gravitational potential energy. However, spring is stretched from its neutral state. As a consequence, there is change in elastic potential energy of the spring. Let “x” be the extension in the spring by the time block of “1 kg” is initiated in motion. Then, the total change in potential energy is :
The work by friction is done only on the right block of “2 kg” :
On the other hand, the work by external force is :
Putting all these values in the equation of conservation of energy :
Clearly, we can not solve this equation as there are two unknowns, “F” and “x”. We, therefore, make use of the fact that spring force on the block of mass “1 kg” is equal to maximum static friction,
Forces on the block
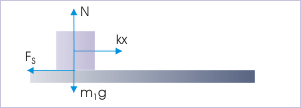
Combining two equations, we have :
Since no external force operates on the system, there is no work by external force. The system under consideration is, therefore, an isolated system. The form of conservation law for general mechanical process is further reduced as :
In words, we can put the conservation of energy for mechanical process under given condition as :
“Work by friction within an isolated system is equal to the change in potential and kinetic energy of the system.”
Problem 2: In the arrangement shown, the block of mass 10 kg descends through a height of 1 m after being released. The coefficient of friction between block and the horizontal table is 0.3, whereas pulley is friction-less. Considering string and pulley to be “mass-less”, find the speed of the blocks.
Block pulley system

Solution : Here, friction is present as internal force to the system. Hence, we use the form of conservation law as :
Let us denote 6 kg and 10 kg blocks with subscript “1” and “2”. There is no change of height for the block on the table. Only change in gravitational potential energy is due to change in the height of the block hanging on the other end of the string. Thus, change in potential energy is :
Two blocks are constrained by a taut string. It means that both blocks move with same speed. Let the speed of the blocks after traveling “1 m” be "v". Now, initial kinetic energy of the system is zero. Therefore, the change in kinetic energy is given by :
Friction works only on the block lying on the table. Here, work by friction is given as :
Putting in the equation of conservation of energy,

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for k-12' conversation and receive update notifications?