| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A 0.100-kg toy car is propelled by a compressed spring, as shown in [link] . The car follows a track that rises 0.180 m above the starting point. The spring is compressed 4.00 cm and has a force constant of 250.0 N/m. Assuming work done by friction to be negligible, find (a) how fast the car is going before it starts up the slope and (b) how fast it is going at the top of the slope.
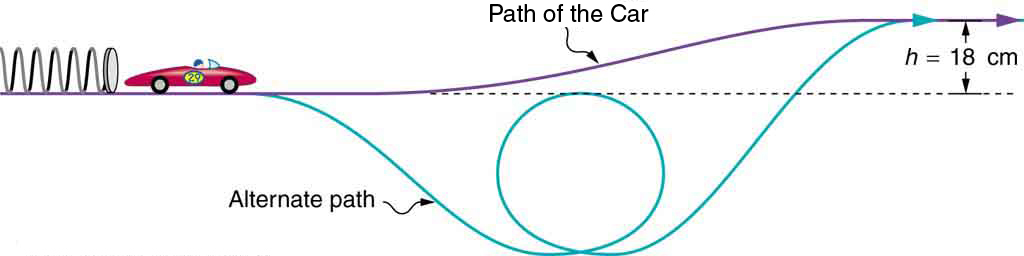
Strategy
The spring force and the gravitational force are conservative forces, so conservation of mechanical energy can be used. Thus,
or
where is the height (vertical position) and is the compression of the spring. This general statement looks complex but becomes much simpler when we start considering specific situations. First, we must identify the initial and final conditions in a problem; then, we enter them into the last equation to solve for an unknown.
Solution for (a)
This part of the problem is limited to conditions just before the car is released and just after it leaves the spring. Take the initial height to be zero, so that both and are zero. Furthermore, the initial speed is zero and the final compression of the spring is zero, and so several terms in the conservation of mechanical energy equation are zero and it simplifies to
In other words, the initial potential energy in the spring is converted completely to kinetic energy in the absence of friction. Solving for the final speed and entering known values yields
Solution for (b)
One method of finding the speed at the top of the slope is to consider conditions just before the car is released and just after it reaches the top of the slope, completely ignoring everything in between. Doing the same type of analysis to find which terms are zero, the conservation of mechanical energy becomes
This form of the equation means that the spring’s initial potential energy is converted partly to gravitational potential energy and partly to kinetic energy. The final speed at the top of the slope will be less than at the bottom. Solving for and substituting known values gives
Discussion
Another way to solve this problem is to realize that the car’s kinetic energy before it goes up the slope is converted partly to potential energy—that is, to take the final conditions in part (a) to be the initial conditions in part (b).
Suppose you are running an experiment in which two 250 g carts connected by a spring (with spring constant 120 N/m) are run into a solid block, and the compression of the spring is measured. In one run of this experiment, the spring was measured to compress from its rest length of 5.0 cm to a minimum length of 2.0 cm. What was the potential energy stored in this system?
Note that the change in length of the spring is 3.0 cm. Hence we can apply Equation 7.42 to find that the potential energy is PE = (1/2)(120 N/m)(0.030 m) 2 = 0.0541 J.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?