| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
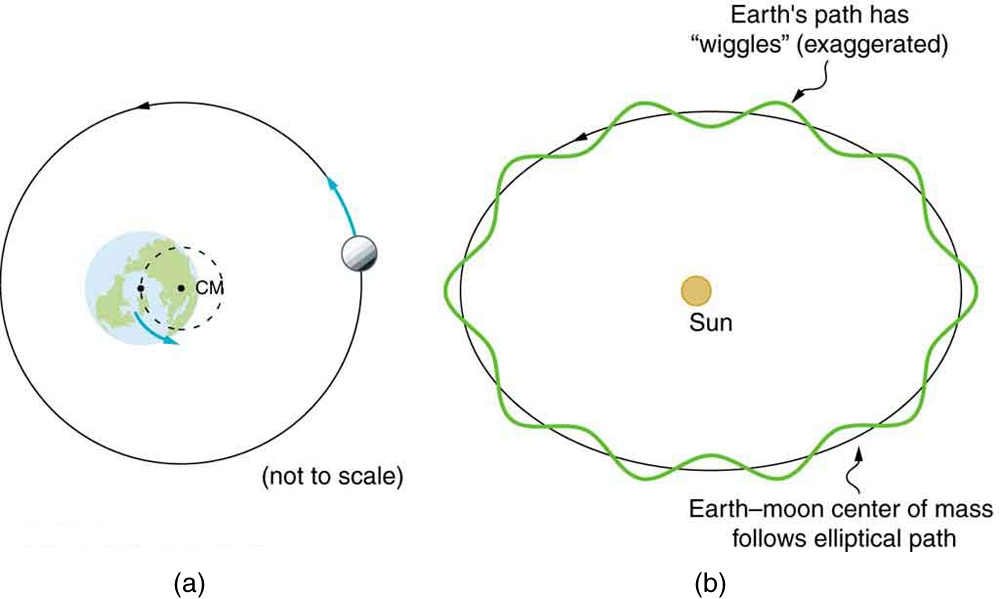
Why does Earth not remain stationary as the Moon orbits it? This is because, as expected from Newton's third law, if Earth exerts a force on the Moon, then the Moon should exert an equal and opposite force on Earth (see [link] ). We do not sense the Moon's effect on Earth's motion, because the Moon's gravity moves our bodies right along with Earth but there are other signs on Earth that clearly show the effect of the Moon's gravitational force as discussed in Satellites and Kepler's Laws: An Argument for Simplicity .
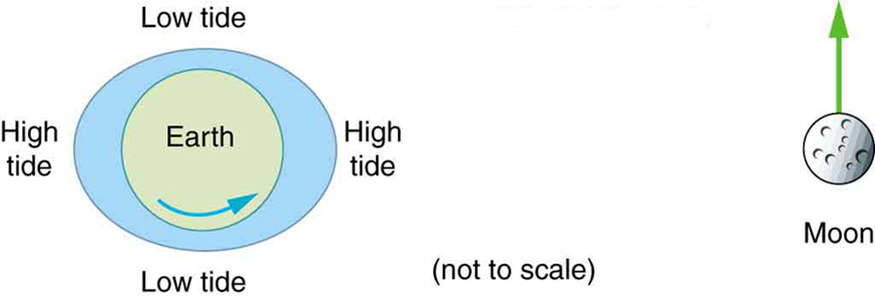
Ocean tides are one very observable result of the Moon's gravity acting on Earth. [link] is a simplified drawing of the Moon's position relative to the tides. Because water easily flows on Earth's surface, a high tide is created on the side of Earth nearest to the Moon, where the Moon's gravitational pull is strongest. Why is there also a high tide on the opposite side of Earth? The answer is that Earth is pulled toward the Moon more than the water on the far side, because Earth is closer to the Moon. So the water on the side of Earth closest to the Moon is pulled away from Earth, and Earth is pulled away from water on the far side. As Earth rotates, the tidal bulge (an effect of the tidal forces between an orbiting natural satellite and the primary planet that it orbits) keeps its orientation with the Moon. Thus there are two tides per day (the actual tidal period is about 12 hours and 25.2 minutes), because the Moon moves in its orbit each day as well).
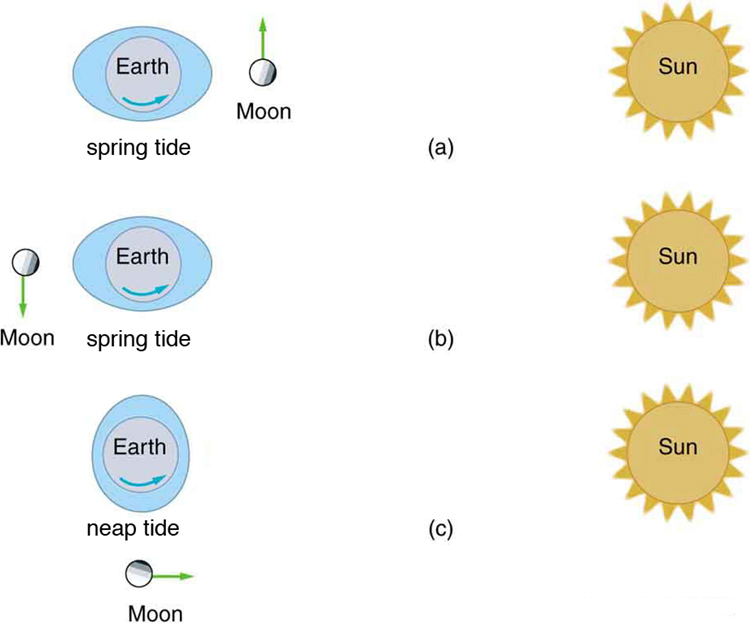
The Sun also affects tides, although it has about half the effect of the Moon. However, the largest tides, called spring tides, occur when Earth, the Moon, and the Sun are aligned. The smallest tides, called neap tides, occur when the Sun is at a angle to the Earth-Moon alignment.
Tides are not unique to Earth but occur in many astronomical systems. The most extreme tides occur where the gravitational force is the strongest and varies most rapidly, such as near black holes (see [link] ). A few likely candidates for black holes have been observed in our galaxy. These have masses greater than the Sun but have diameters only a few kilometers across. The tidal forces near them are so great that they can actually tear matter from a companion star.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?