| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Why does light change direction when passing from one material (medium) to another? It is because light changes speed when going from one material to another. So before we study the law of refraction, it is useful to discuss the speed of light and how it varies in different media.
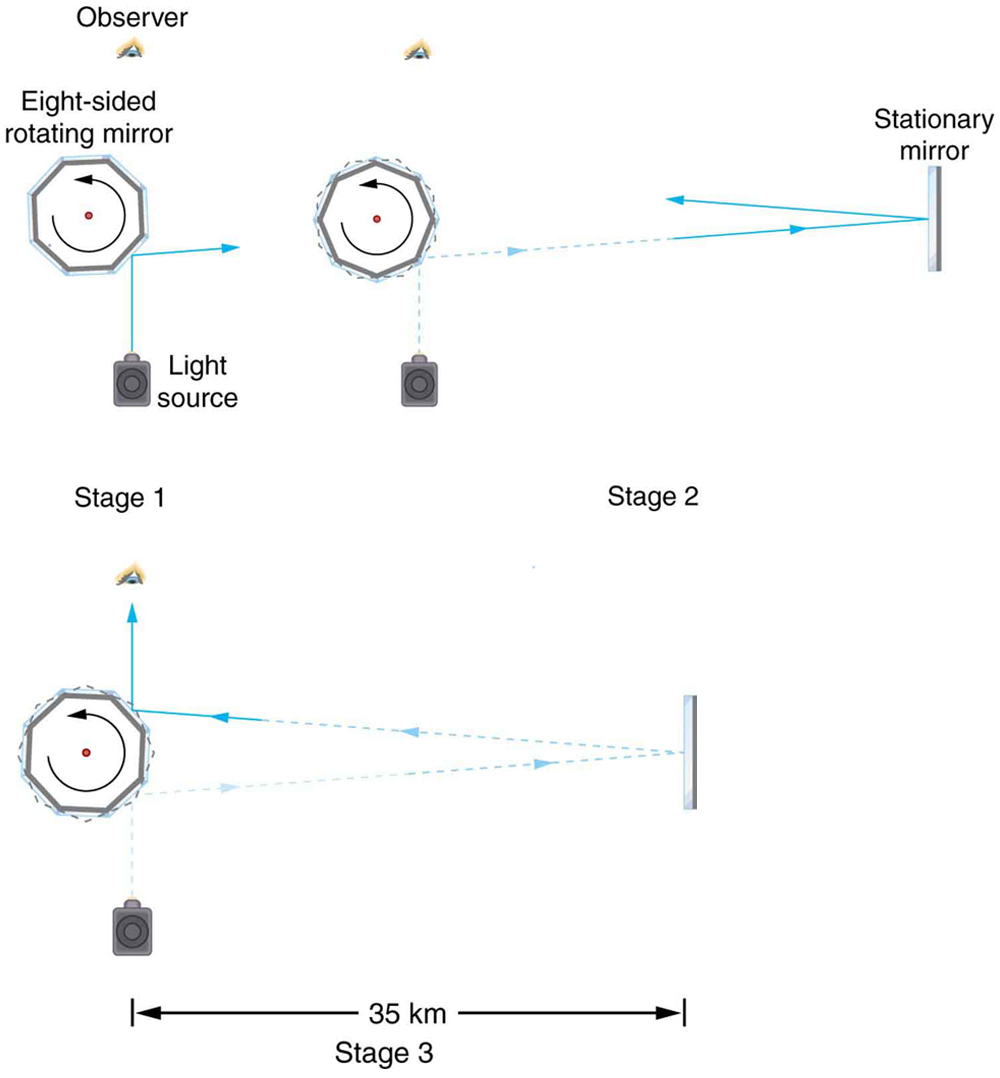
Early attempts to measure the speed of light, such as those made by Galileo, determined that light moved extremely fast, perhaps instantaneously. The first real evidence that light traveled at a finite speed came from the Danish astronomer Ole Roemer in the late 17th century. Roemer had noted that the average orbital period of one of Jupiter’s moons, as measured from Earth, varied depending on whether Earth was moving toward or away from Jupiter. He correctly concluded that the apparent change in period was due to the change in distance between Earth and Jupiter and the time it took light to travel this distance. From his 1676 data, a value of the speed of light was calculated to be (only 25% different from today’s accepted value). In more recent times, physicists have measured the speed of light in numerous ways and with increasing accuracy. One particularly direct method, used in 1887 by the American physicist Albert Michelson (1852–1931), is illustrated in [link] . Light reflected from a rotating set of mirrors was reflected from a stationary mirror 35 km away and returned to the rotating mirrors. The time for the light to travel can be determined by how fast the mirrors must rotate for the light to be returned to the observer’s eye.
The speed of light is now known to great precision. In fact, the speed of light in a vacuum is so important that it is accepted as one of the basic physical quantities and has the fixed value
where the approximate value of is used whenever three-digit accuracy is sufficient. The speed of light through matter is less than it is in a vacuum, because light interacts with atoms in a material. The speed of light depends strongly on the type of material, since its interaction with different atoms, crystal lattices, and other substructures varies. We define the index of refraction of a material to be
where is the observed speed of light in the material. Since the speed of light is always less than in matter and equals only in a vacuum, the index of refraction is always greater than or equal to one.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?