| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
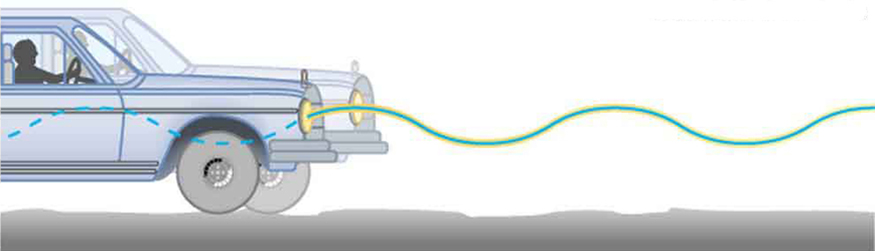
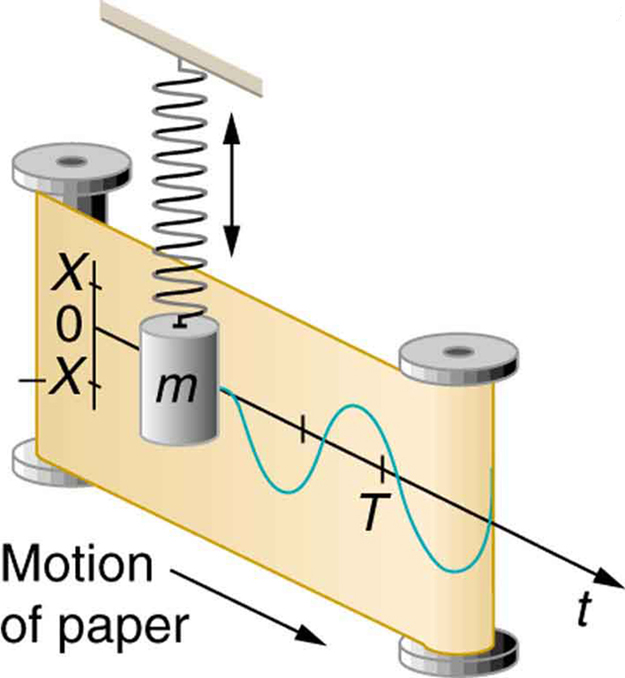
If a time-exposure photograph of the bouncing car were taken as it drove by, the headlight would make a wavelike streak, as shown in [link] . Similarly, [link] shows an object bouncing on a spring as it leaves a wavelike "trace of its position on a moving strip of paper. Both waves are sine functions. All simple harmonic motion is intimately related to sine and cosine waves.
The displacement as a function of time t in any simple harmonic motion—that is, one in which the net restoring force can be described by Hooke’s law, is given by
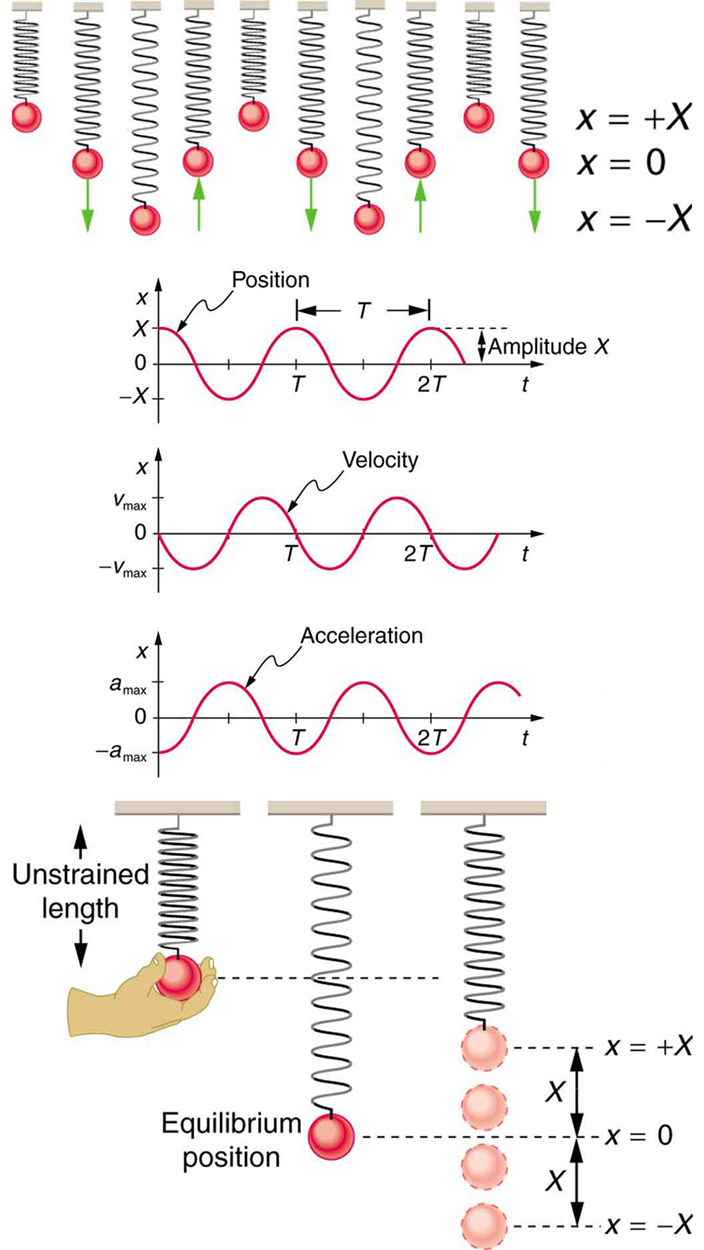
where is amplitude. At , the initial position is , and the displacement oscillates back and forth with a period . (When , we get again because .). Furthermore, from this expression for , the velocity as a function of time is given by:
where . The object has zero velocity at maximum displacement—for example, when , and at that time . The minus sign in the first equation for gives the correct direction for the velocity. Just after the start of the motion, for instance, the velocity is negative because the system is moving back toward the equilibrium point. Finally, we can get an expression for acceleration using Newton’s second law. [Then we have and , the quantities needed for kinematics and a description of simple harmonic motion.] According to Newton’s second law, the acceleration is . So, is also a cosine function:
Hence, is directly proportional to and in the opposite direction to .
[link] shows the simple harmonic motion of an object on a spring and presents graphs of and versus time.
The most important point here is that these equations are mathematically straightforward and are valid for all simple harmonic motion. They are very useful in visualizing waves associated with simple harmonic motion, including visualizing how waves add with one another.
Suppose you pluck a banjo string. You hear a single note that starts out loud and slowly quiets over time. Describe what happens to the sound waves in terms of period, frequency and amplitude as the sound decreases in volume.
Frequency and period remain essentially unchanged. Only amplitude decreases as volume decreases.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?