| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Suppose that in a situation like that in [link] , light goes from air to diamond and that the incident angle is . Calculate the angle of refraction in the diamond.
Strategy
Again the index of refraction for air is taken to be , and we are given . We can look up the index of refraction for diamond in [link] , finding . The only unknown in Snell’s law is , which we wish to determine.
Solution
Solving Snell’s law for sin yields
Entering known values,
The angle is thus
Discussion
For the same angle of incidence, the angle of refraction in diamond is significantly smaller than in water ( rather than —see the preceding example). This means there is a larger change in direction in diamond. The cause of a large change in direction is a large change in the index of refraction (or speed). In general, the larger the change in speed, the greater the effect on the direction of the ray.
When light travels from air into water, which of the following statements is accurate?
(a)
When a light ray travels from air into glass, which of the following statements is accurate after the light enters the glass?
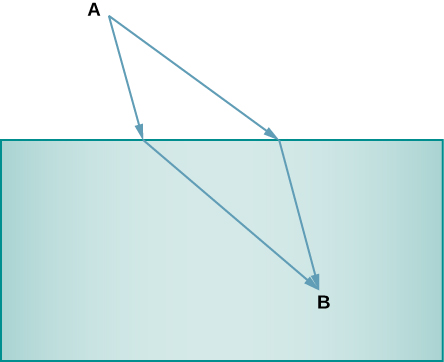
Two different potential paths from point A to point B are shown. Point A is in the air, and point B is in water. For which of these paths (upper or lower) would light travel from point A to point B faster? Which of the paths more accurately represents how a light ray would travel from point A to point B? Explain.
Since light bends toward the normal upon entering a medium with a higher index of refraction, the upper path is a more accurate representation of a light ray moving from A to B.
Students in a lab group are given a plastic cube with a hollow cube-shaped space in the middle that fills about half the volume of the cube. The index of refraction of the plastic is known. The hollow space is filled with a gas, and the students are asked to collect the data needed to find the index of refraction of the gas. The students take the following set of measurements:
Angle of incidence of the light in the air above the plastic block: 30°
Angle of refraction of the beam as it enters the plastic from the air: 45°
Angle of refraction of the beam as it enters the plastic from the gas: 45°
The three measurements are shared with a second lab group. Can the second group determine a value for the index of refraction of the gas from only this data?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?