| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
|
|
Resistivity ( ) |
|---|---|
| Conductors | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Semiconductors Values depend strongly on amounts and types of impurities | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Insulators | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A car headlight filament is made of tungsten and has a cold resistance of . If the filament is a cylinder 4.00 cm long (it may be coiled to save space), what is its diameter?
Strategy
We can rearrange the equation to find the cross-sectional area of the filament from the given information. Then its diameter can be found by assuming it has a circular cross-section.
Solution
The cross-sectional area, found by rearranging the expression for the resistance of a cylinder given in , is
Substituting the given values, and taking from [link] , yields
The area of a circle is related to its diameter by
Solving for the diameter , and substituting the value found for , gives
Discussion
The diameter is just under a tenth of a millimeter. It is quoted to only two digits, because is known to only two digits.
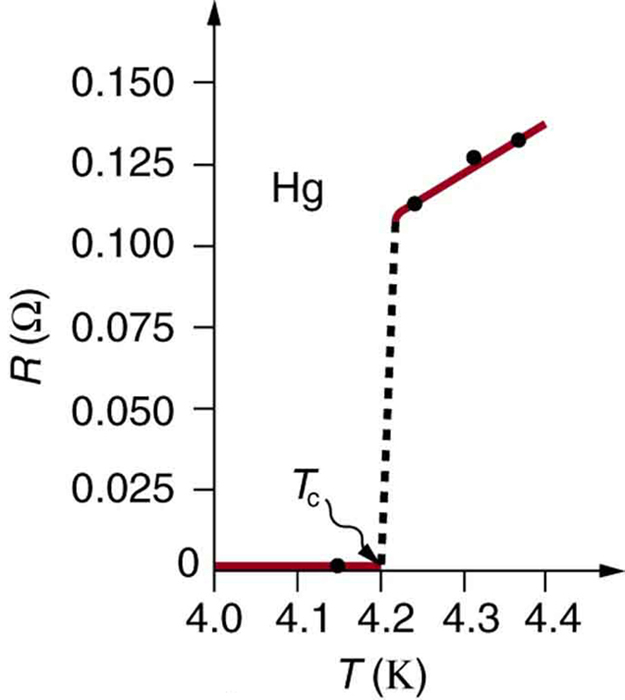
The resistivity of all materials depends on temperature. Some even become superconductors (zero resistivity) at very low temperatures. (See [link] .) Conversely, the resistivity of conductors increases with increasing temperature. Since the atoms vibrate more rapidly and over larger distances at higher temperatures, the electrons moving through a metal make more collisions, effectively making the resistivity higher. Over relatively small temperature changes (about or less), resistivity varies with temperature change as expressed in the following equation
where is the original resistivity and is the temperature coefficient of resistivity . (See the values of in [link] below.) For larger temperature changes, may vary or a nonlinear equation may be needed to find . Note that is positive for metals, meaning their resistivity increases with temperature. Some alloys have been developed specifically to have a small temperature dependence. Manganin (which is made of copper, manganese and nickel), for example, has close to zero (to three digits on the scale in [link] ), and so its resistivity varies only slightly with temperature. This is useful for making a temperature-independent resistance standard, for example.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?