| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |


Thermometers are used to measure temperature according to well-defined scales of measurement, which use pre-defined reference points to help compare quantities. The three most common temperature scales are the Fahrenheit, Celsius, and Kelvin scales. A temperature scale can be created by identifying two easily reproducible temperatures. The freezing and boiling temperatures of water at standard atmospheric pressure are commonly used.
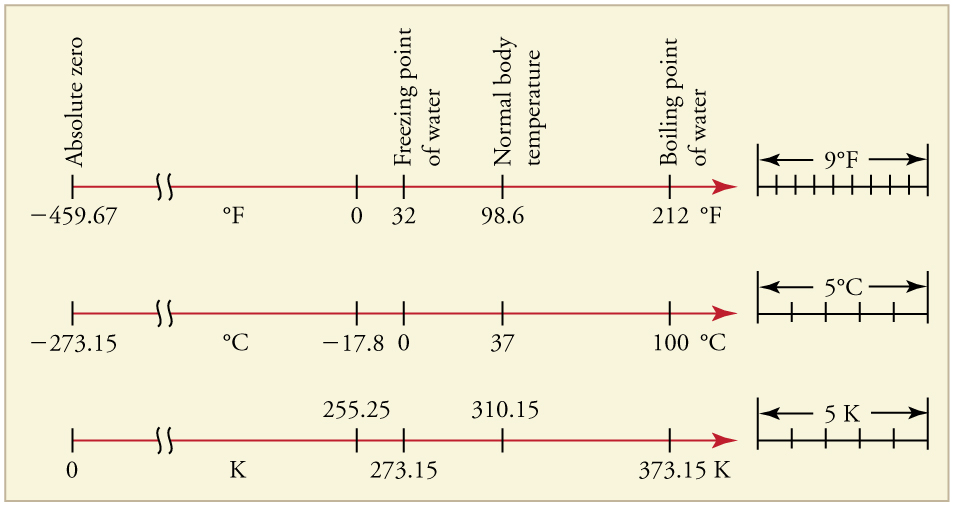
The Celsius scale (which replaced the slightly different centigrade scale) has the freezing point of water at and the boiling point at . Its unit is the degree Celsius . On the Fahrenheit scale (still the most frequently used in the United States), the freezing point of water is at and the boiling point is at . The unit of temperature on this scale is the degree Fahrenheit . Note that a temperature difference of one degree Celsius is greater than a temperature difference of one degree Fahrenheit. Only 100 Celsius degrees span the same range as 180 Fahrenheit degrees, thus one degree on the Celsius scale is 1.8 times larger than one degree on the Fahrenheit scale
The Kelvin scale is the temperature scale that is commonly used in science. It is an absolute temperature scale defined to have 0 K at the lowest possible temperature, called absolute zero . The official temperature unit on this scale is the kelvin , which is abbreviated K, and is not accompanied by a degree sign. The freezing and boiling points of water are 273.15 K and 373.15 K, respectively. Thus, the magnitude of temperature differences is the same in units of kelvins and degrees Celsius. Unlike other temperature scales, the Kelvin scale is an absolute scale. It is used extensively in scientific work because a number of physical quantities, such as the volume of an ideal gas, are directly related to absolute temperature. The kelvin is the SI unit used in scientific work.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?