| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Perhaps the most important thing to note about these examples is the signs of the answers. In our chosen coordinate system, plus means the quantity is to the right and minus means it is to the left. This is easy to imagine for displacement and velocity. But it is a little less obvious for acceleration. Most people interpret negative acceleration as the slowing of an object. This was not the case in [link] , where a positive acceleration slowed a negative velocity. The crucial distinction was that the acceleration was in the opposite direction from the velocity. In fact, a negative acceleration will increase a negative velocity. For example, the train moving to the left in [link] is sped up by an acceleration to the left. In that case, both and are negative. The plus and minus signs give the directions of the accelerations. If acceleration has the same sign as the velocity, the object is speeding up. If acceleration has the opposite sign as the velocity, the object is slowing down.
An airplane lands on a runway traveling east. Describe its acceleration.
If we take east to be positive, then the airplane has negative acceleration, as it is accelerating toward the west. It is also decelerating: its acceleration is opposite in direction to its velocity.
Learn about position, velocity, and acceleration graphs. Move the little man back and forth with the mouse and plot his motion. Set the position, velocity, or acceleration and let the simulation move the man for you.

Is it possible for speed to be constant while acceleration is not zero? Give an example of such a situation.
Is it possible for velocity to be constant while acceleration is not zero? Explain.
Give an example in which velocity is zero yet acceleration is not.
If a subway train is moving to the left (has a negative velocity) and then comes to a stop, what is the direction of its acceleration? Is the acceleration positive or negative?
Plus and minus signs are used in one-dimensional motion to indicate direction. What is the sign of an acceleration that reduces the magnitude of a negative velocity? Of a positive velocity?
A cheetah can accelerate from rest to a speed of 30.0 m/s in 7.00 s. What is its acceleration?
Professional Application
Dr. John Paul Stapp was U.S. Air Force officer who studied the effects of extreme deceleration on the human body. On December 10, 1954, Stapp rode a rocket sled, accelerating from rest to a top speed of 282 m/s (1015 km/h) in 5.00 s, and was brought jarringly back to rest in only 1.40 s! Calculate his (a) acceleration and (b) deceleration. Express each in multiples of by taking its ratio to the acceleration of gravity.
A commuter backs her car out of her garage with an acceleration of . (a) How long does it take her to reach a speed of 2.00 m/s? (b) If she then brakes to a stop in 0.800 s, what is her deceleration?
(a)
(b)
Assume that an intercontinental ballistic missile goes from rest to a suborbital speed of 6.50 km/s in 60.0 s (the actual speed and time are classified). What is its average acceleration in and in multiples of
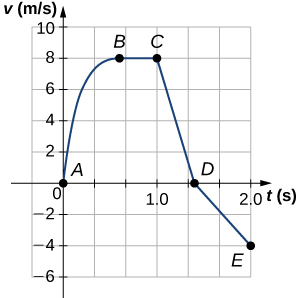
A cart is constrained to move along a straight line. A varying net force along the direction of motion is exerted on the cart. The cart's velocity v as a function of time t is shown in the graph. The five labeled points divide the graph into four sections.
Which of the following correctly ranks the magnitude of the average acceleration of the cart during the four sections of the graph?
Push a book across a table and observe it slow to a stop.
Draw graphs showing the book's position vs. time and velocity vs. time if the direction of its motion is considered positive.
Draw graphs showing the book's position vs. time and velocity vs. time if the direction of its motion is considered negative.
The position vs. time graph should be represented with a positively sloped line whose slope steadily decreases to zero. The y -intercept of the graph may be any value. The line on the velocity vs. time graph should have a positive y -intercept and a negative slope. Because the final velocity of the book is zero, the line should finish on the x -axis.
The position vs. time graph should be represented with a negatively sloped line whose slope steadily decreases to zero. The y -intercept of the graph may be any value. The line on the velocity vs. time graph should have a negative y -intercept and a positive slope. Because the final velocity of the book is zero, the line should finish on the x -axis.]

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?