| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
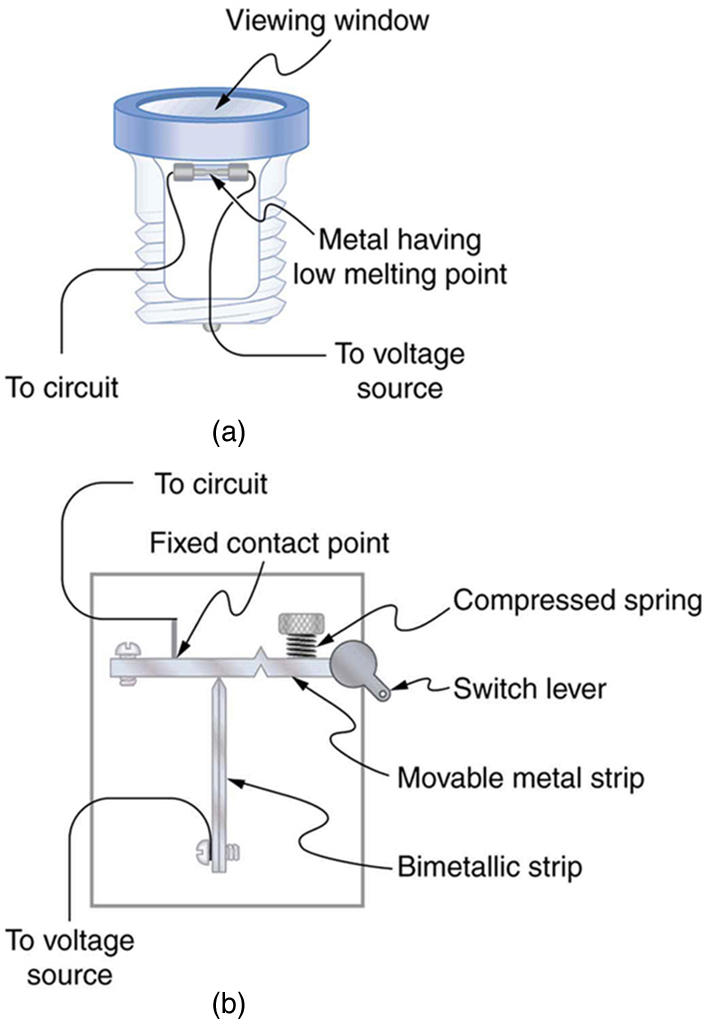
Fuses and circuit breakers for typical household voltages and currents are relatively simple to produce, but those for large voltages and currents experience special problems. For example, when a circuit breaker tries to interrupt the flow of high-voltage electricity, a spark can jump across its points that ionizes the air in the gap and allows the current to continue. Large circuit breakers found in power-distribution systems employ insulating gas and even use jets of gas to blow out such sparks. Here AC is safer than DC, since AC current goes through zero 120 times per second, giving a quick opportunity to extinguish these arcs.
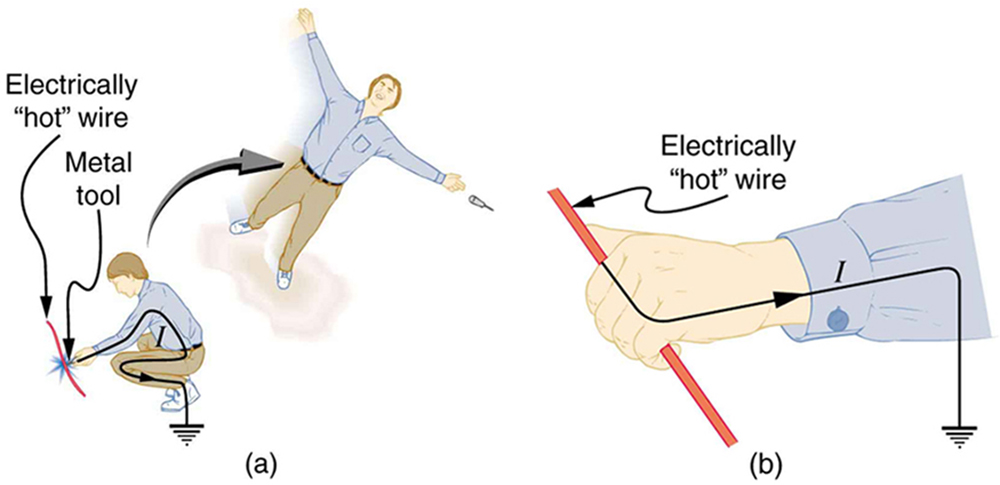
Electrical currents through people produce tremendously varied effects. An electrical current can be used to block back pain. The possibility of using electrical current to stimulate muscle action in paralyzed limbs, perhaps allowing paraplegics to walk, is under study. TV dramatizations in which electrical shocks are used to bring a heart attack victim out of ventricular fibrillation (a massively irregular, often fatal, beating of the heart) are more than common. Yet most electrical shock fatalities occur because a current put the heart into fibrillation. A pacemaker uses electrical shocks to stimulate the heart to beat properly. Some fatal shocks do not produce burns, but warts can be safely burned off with electric current (though freezing using liquid nitrogen is now more common). Of course, there are consistent explanations for these disparate effects. The major factors upon which the effects of electrical shock depend are
[link] gives the effects of electrical shocks as a function of current for a typical accidental shock. The effects are for a shock that passes through the trunk of the body, has a duration of 1 s, and is caused by 60-Hz power.
| Current (mA) | Effect |
|---|---|
| 1 | Threshold of sensation |
| 5 | Maximum harmless current |
| 10–20 | Onset of sustained muscular contraction; cannot let go for duration of shock; contraction of chest muscles may stop breathing during shock |
| 50 | Onset of pain |
| 100–300+ | Ventricular fibrillation possible; often fatal |
| 300 | Onset of burns depending on concentration of current |
| 6000 (6 A) | Onset of sustained ventricular contraction and respiratory paralysis; both cease when shock ends; heartbeat may return to normal; used to defibrillate the heart |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?