| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Converting this to eV by multiplying by yields
The photon energy is
which is about five orders of magnitude greater.
Discussion
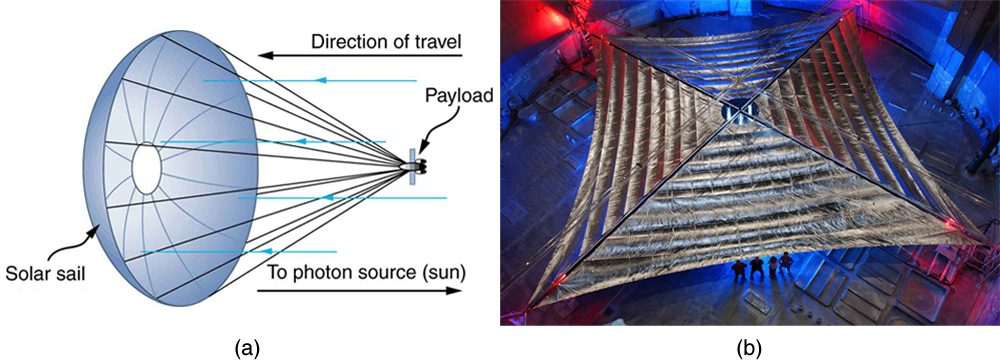
Photon momentum is indeed small. Even if we have huge numbers of them, the total momentum they carry is small. An electron with the same momentum has a 1460 m/s velocity, which is clearly nonrelativistic. A more massive particle with the same momentum would have an even smaller velocity. This is borne out by the fact that it takes far less energy to give an electron the same momentum as a photon. But on a quantum-mechanical scale, especially for high-energy photons interacting with small masses, photon momentum is significant. Even on a large scale, photon momentum can have an effect if there are enough of them and if there is nothing to prevent the slow recoil of matter. Comet tails are one example, but there are also proposals to build space sails that use huge low-mass mirrors (made of aluminized Mylar) to reflect sunlight. In the vacuum of space, the mirrors would gradually recoil and could actually take spacecraft from place to place in the solar system. (See [link] .)
There is a relationship between photon momentum and photon energy that is consistent with the relation given previously for the relativistic total energy of a particle as . We know is zero for a photon, but is not, so that becomes
or
To check the validity of this relation, note that for a photon. Substituting this into yields
as determined experimentally and discussed above. Thus, is equivalent to Compton’s result . For a further verification of the relationship between photon energy and momentum, see [link] .
Almost all detection systems talked about thus far—eyes, photographic plates, photomultiplier tubes in microscopes, and CCD cameras—rely on particle-like properties of photons interacting with a sensitive area. A change is caused and either the change is cascaded or zillions of points are recorded to form an image we detect. These detectors are used in biomedical imaging systems, and there is ongoing research into improving the efficiency of receiving photons, particularly by cooling detection systems and reducing thermal effects.
Show that for the photon considered in the [link] .
Strategy
We will take the energy found in [link] , divide it by the speed of light, and see if the same momentum is obtained as before.
Solution
Given that the energy of the photon is 2.48 eV and converting this to joules, we get
Discussion
This value for momentum is the same as found before (note that unrounded values are used in all calculations to avoid even small rounding errors), an expected verification of the relationship . This also means the relationship between energy, momentum, and mass given by applies to both matter and photons. Once again, note that is not zero, even when is.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?