| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
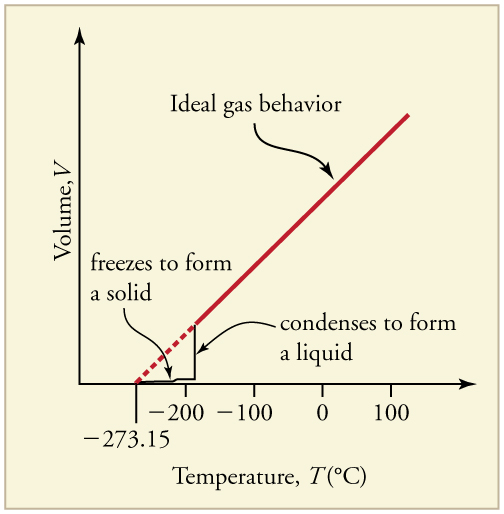
Up to now, we have considered the behavior of ideal gases. Real gases are like ideal gases at high temperatures. At lower temperatures, however, the interactions between the molecules and their volumes cannot be ignored. The molecules are very close (condensation occurs) and there is a dramatic decrease in volume, as seen in [link] . The substance changes from a gas to a liquid. When a liquid is cooled to even lower temperatures, it becomes a solid. The volume never reaches zero because of the finite volume of the molecules.
High pressure may also cause a gas to change phase to a liquid. Carbon dioxide, for example, is a gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, but becomes a liquid under sufficiently high pressure. If the pressure is reduced, the temperature drops and the liquid carbon dioxide solidifies into a snow-like substance at the temperature . Solid is called “dry ice.” Another example of a gas that can be in a liquid phase is liquid nitrogen . is made by liquefaction of atmospheric air (through compression and cooling). It boils at 77 K at atmospheric pressure. is useful as a refrigerant and allows for the preservation of blood, sperm, and other biological materials. It is also used to reduce noise in electronic sensors and equipment, and to help cool down their current-carrying wires. In dermatology, is used to freeze and painlessly remove warts and other growths from the skin.
We can examine aspects of the behavior of a substance by plotting a graph of pressure versus volume, called a PV diagram . When the substance behaves like an ideal gas, the ideal gas law describes the relationship between its pressure and volume. That is,
Now, assuming the number of molecules and the temperature are fixed,
For example, the volume of the gas will decrease as the pressure increases. If you plot the relationship on a diagram, you find a hyperbola. [link] shows a graph of pressure versus volume. The hyperbolas represent ideal-gas behavior at various fixed temperatures, and are called isotherms . At lower temperatures, the curves begin to look less like hyperbolas—the gas is not behaving ideally and may even contain liquid. There is a critical point —that is, a critical temperature —above which liquid cannot exist. At sufficiently high pressure above the critical point, the gas will have the density of a liquid but will not condense. Carbon dioxide, for example, cannot be liquefied at a temperature above . Critical pressure is the minimum pressure needed for liquid to exist at the critical temperature. [link] lists representative critical temperatures and pressures.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?