| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A babysitter is pushing a child on a swing. At the point where the swing reaches , where would the corresponding point on a wave of this motion be located?
is the maximum deformation, which corresponds to the amplitude of the wave. The point on the wave would either be at the very top or the very bottom of the curve.
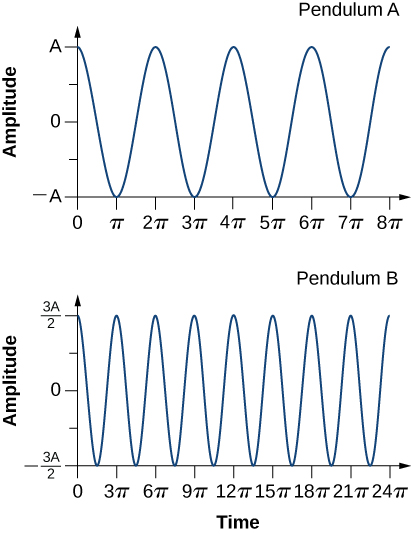
Use these figures to answer the following questions.
A particle of mass 100 g undergoes a simple harmonic motion. The restoring force is provided by a spring with a spring constant of 40 N∙m −1 . What is the period of oscillation?
(c)
The graph shows the simple harmonic motion of a mass m attached to a spring with spring constant k .
What is the displacement at time 8 π ?
A pendulum of mass 200 g undergoes simple harmonic motion when acted upon by a force of 15 N. The pendulum crosses the point of equilibrium at a speed of 5 m∙s −1 . What is the energy of the pendulum at the center of the oscillation?
The energy of the particle at the center of the oscillation is given by
A realistic mass and spring laboratory. Hang masses from springs and adjust the spring stiffness and damping. You can even slow time. Transport the lab to different planets. A chart shows the kinetic, potential, and thermal energy for each spring.

and , where is the mass of the system.
What conditions must be met to produce simple harmonic motion?
(a) If frequency is not constant for some oscillation, can the oscillation be simple harmonic motion?
(b) Can you think of any examples of harmonic motion where the frequency may depend on the amplitude?
Give an example of a simple harmonic oscillator, specifically noting how its frequency is independent of amplitude.
Explain why you expect an object made of a stiff material to vibrate at a higher frequency than a similar object made of a spongy material.
As you pass a freight truck with a trailer on a highway, you notice that its trailer is bouncing up and down slowly. Is it more likely that the trailer is heavily loaded or nearly empty? Explain your answer.
Some people modify cars to be much closer to the ground than when manufactured. Should they install stiffer springs? Explain your answer.
A type of cuckoo clock keeps time by having a mass bouncing on a spring, usually something cute like a cherub in a chair. What force constant is needed to produce a period of 0.500 s for a 0.0150-kg mass?
If the spring constant of a simple harmonic oscillator is doubled, by what factor will the mass of the system need to change in order for the frequency of the motion to remain the same?
A 0.500-kg mass suspended from a spring oscillates with a period of 1.50 s. How much mass must be added to the object to change the period to 2.00 s?
0.389 kg
By how much leeway (both percentage and mass) would you have in the selection of the mass of the object in the previous problem if you did not wish the new period to be greater than 2.01 s or less than 1.99 s?
Suppose you attach the object with mass to a vertical spring originally at rest, and let it bounce up and down. You release the object from rest at the spring’s original rest length. (a) Show that the spring exerts an upward force of on the object at its lowest point. (b) If the spring has a force constant of and a 0.25-kg-mass object is set in motion as described, find the amplitude of the oscillations. (c) Find the maximum velocity.
A diver on a diving board is undergoing simple harmonic motion. Her mass is 55.0 kg and the period of her motion is 0.800 s. The next diver is a male whose period of simple harmonic oscillation is 1.05 s. What is his mass if the mass of the board is negligible?
94.7 kg
Suppose a diving board with no one on it bounces up and down in a simple harmonic motion with a frequency of 4.00 Hz. The board has an effective mass of 10.0 kg. What is the frequency of the simple harmonic motion of a 75.0-kg diver on the board?
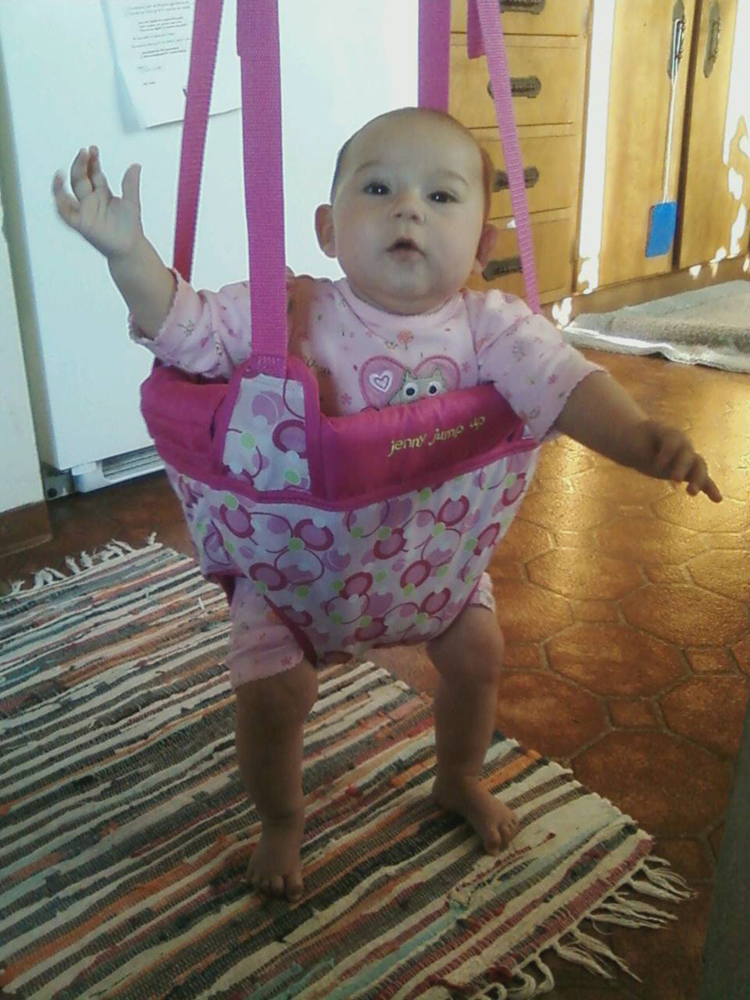

The device pictured in [link] entertains infants while keeping them from wandering. The child bounces in a harness suspended from a door frame by a spring constant.
(a) If the spring stretches 0.250 m while supporting an 8.0-kg child, what is its spring constant?
(b) What is the time for one complete bounce of this child? (c) What is the child’s maximum velocity if the amplitude of her bounce is 0.200 m?
A 90.0-kg skydiver hanging from a parachute bounces up and down with a period of 1.50 s. What is the new period of oscillation when a second skydiver, whose mass is 60.0 kg, hangs from the legs of the first, as seen in [link] .
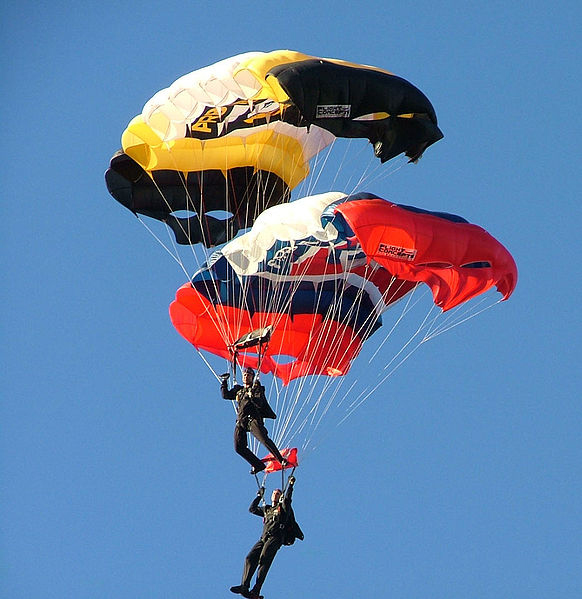

1.94 s

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?