| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
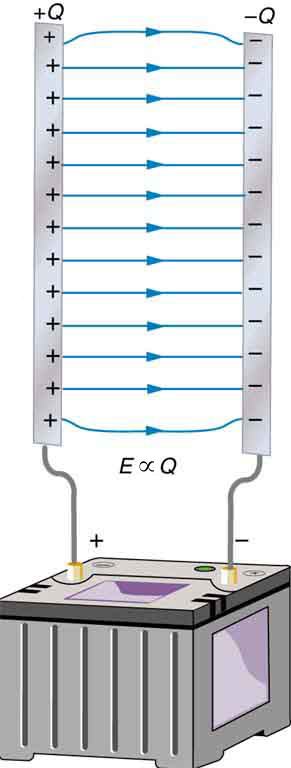
The field is proportional to the charge:
where the symbol means “proportional to.” From the discussion in Electric Potential in a Uniform Electric Field , we know that the voltage across parallel plates is . Thus,
It follows, then, that , and conversely,
This is true in general: The greater the voltage applied to any capacitor, the greater the charge stored in it.
Different capacitors will store different amounts of charge for the same applied voltage, depending on their physical characteristics. We define their capacitance to be such that the charge stored in a capacitor is proportional to . The charge stored in a capacitor is given by
This equation expresses the two major factors affecting the amount of charge stored. Those factors are the physical characteristics of the capacitor, , and the voltage, . Rearranging the equation, we see that capacitance is the amount of charge stored per volt, or
Capacitance is the amount of charge stored per volt, or
The unit of capacitance is the farad (F), named for Michael Faraday (1791–1867), an English scientist who contributed to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. Since capacitance is charge per unit voltage, we see that a farad is a coulomb per volt, or
A 1-farad capacitor would be able to store 1 coulomb (a very large amount of charge) with the application of only 1 volt. One farad is, thus, a very large capacitance. Typical capacitors range from fractions of a picofarad to millifarads .
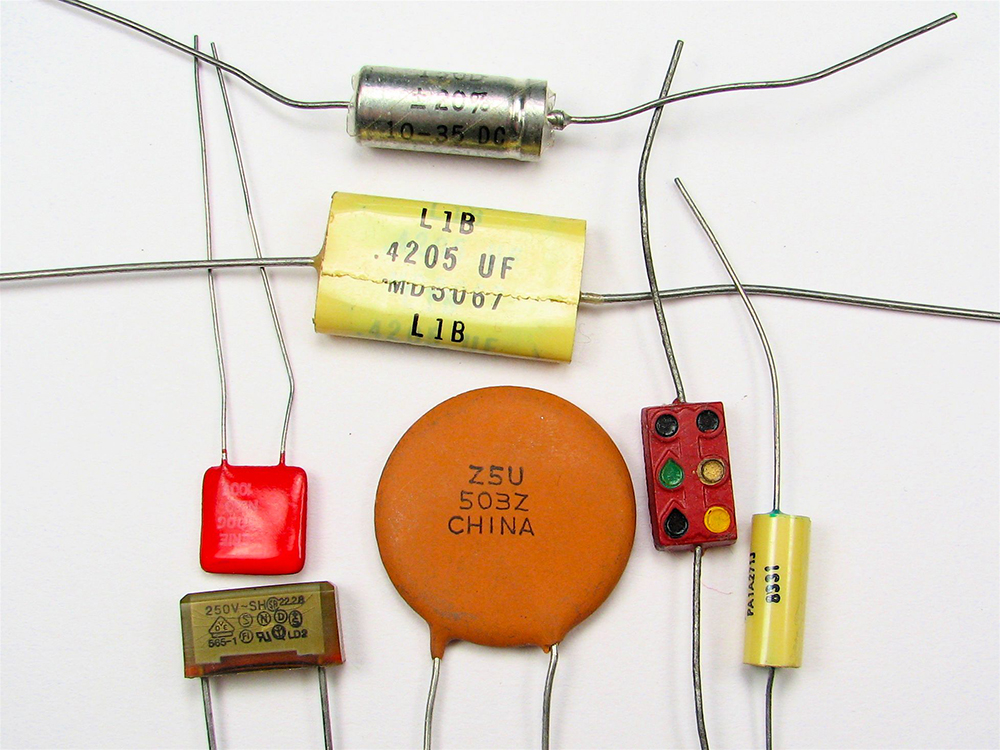
[link] shows some common capacitors. Capacitors are primarily made of ceramic, glass, or plastic, depending upon purpose and size. Insulating materials, called dielectrics, are commonly used in their construction, as discussed below.
The parallel plate capacitor shown in [link] has two identical conducting plates, each having a surface area , separated by a distance (with no material between the plates). When a voltage is applied to the capacitor, it stores a charge , as shown. We can see how its capacitance depends on and by considering the characteristics of the Coulomb force. We know that like charges repel, unlike charges attract, and the force between charges decreases with distance. So it seems quite reasonable that the bigger the plates are, the more charge they can store—because the charges can spread out more. Thus should be greater for larger . Similarly, the closer the plates are together, the greater the attraction of the opposite charges on them. So should be greater for smaller .


Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?