| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
The information presented in this section supports the following AP® learning objectives and science practices:
Forces are either conservative or nonconservative. Conservative forces were discussed in Conservative Forces and Potential Energy . A nonconservative force is one for which work depends on the path taken. Friction is a good example of a nonconservative force. As illustrated in [link] , work done against friction depends on the length of the path between the starting and ending points. Because of this dependence on path, there is no potential energy associated with nonconservative forces. An important characteristic is that the work done by a nonconservative force adds or removes mechanical energy from a system . Friction , for example, creates thermal energy that dissipates, removing energy from the system. Furthermore, even if the thermal energy is retained or captured, it cannot be fully converted back to work, so it is lost or not recoverable in that sense as well.
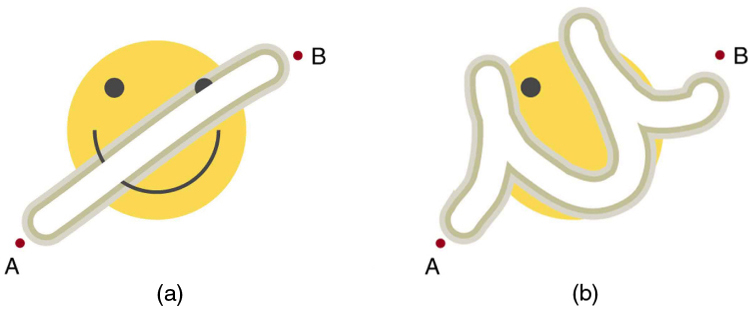
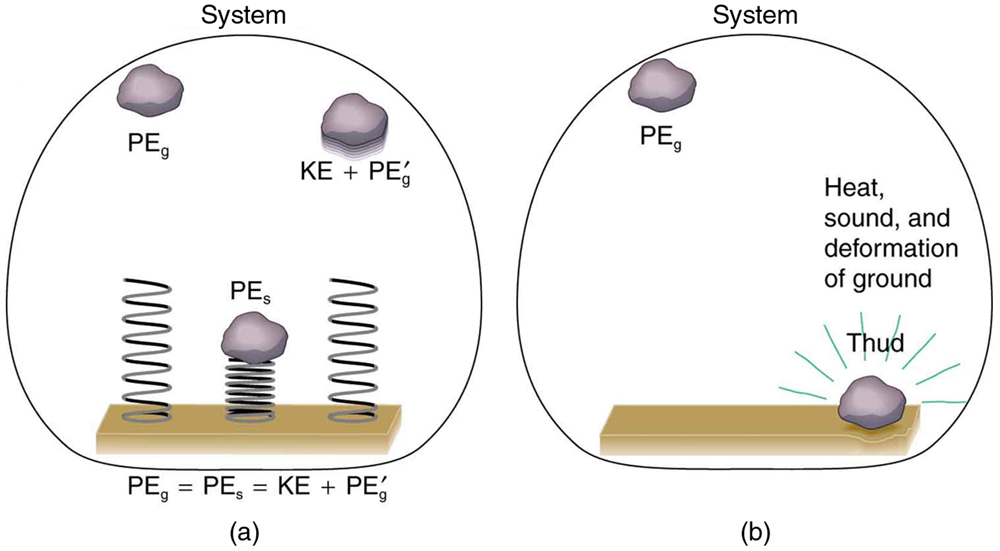
Mechanical energy may not be conserved when nonconservative forces act. For example, when a car is brought to a stop by friction on level ground, it loses kinetic energy, which is dissipated as thermal energy, reducing its mechanical energy. [link] compares the effects of conservative and nonconservative forces. We often choose to understand simpler systems such as that described in [link] (a) first before studying more complicated systems as in [link] (b).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?