| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
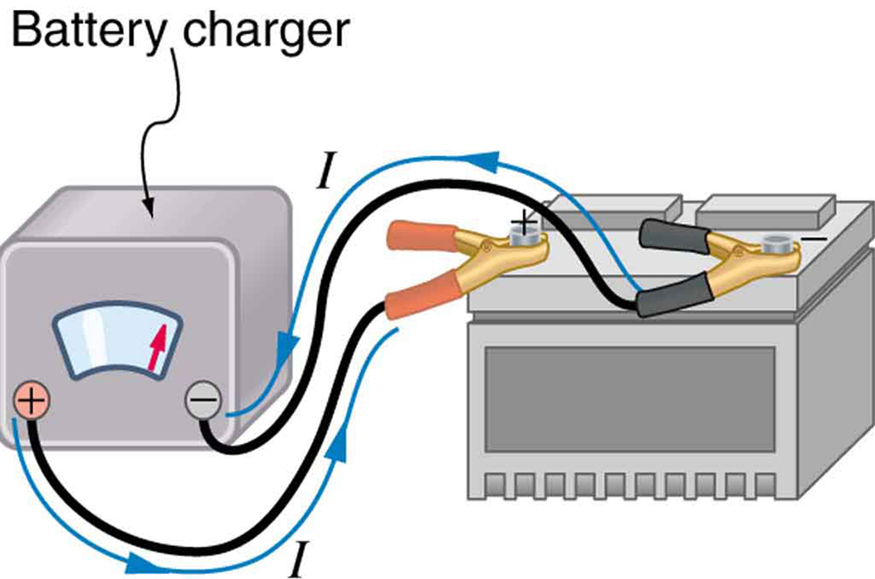
Some batteries can be recharged by passing a current through them in the direction opposite to the current they supply to a resistance. This is done routinely in cars and batteries for small electrical appliances and electronic devices, and is represented pictorially in [link] . The voltage output of the battery charger must be greater than the emf of the battery to reverse current through it. This will cause the terminal voltage of the battery to be greater than the emf, since , and is now negative.
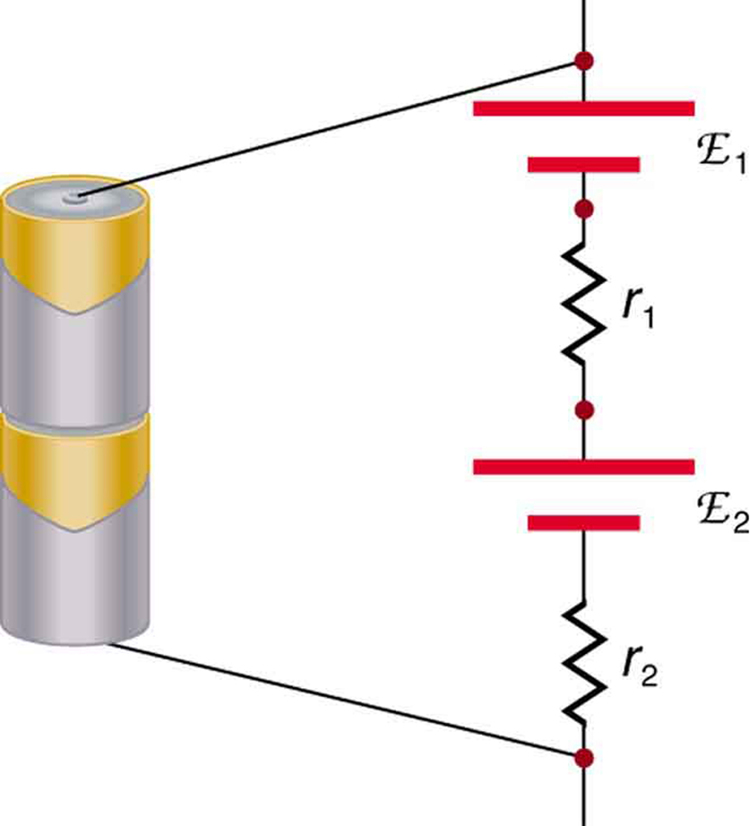
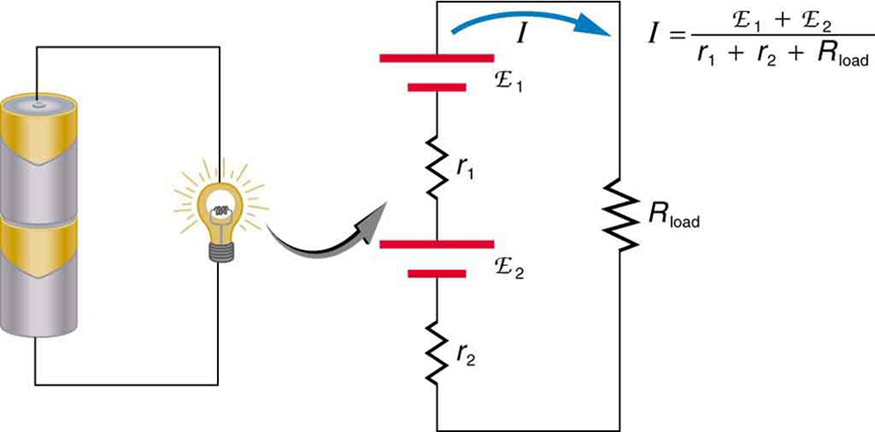
There are two voltage sources when a battery charger is used. Voltage sources connected in series are relatively simple. When voltage sources are in series, their internal resistances add and their emfs add algebraically. (See [link] .) Series connections of voltage sources are common—for example, in flashlights, toys, and other appliances. Usually, the cells are in series in order to produce a larger total emf.
But if the cells oppose one another, such as when one is put into an appliance backward, the total emf is less, since it is the algebraic sum of the individual emfs.
A battery is a multiple connection of voltaic cells, as shown in [link] . The disadvantage of series connections of cells is that their internal resistances add. One of the authors once owned a 1957 MGA that had two 6-V batteries in series, rather than a single 12-V battery. This arrangement produced a large internal resistance that caused him many problems in starting the engine.
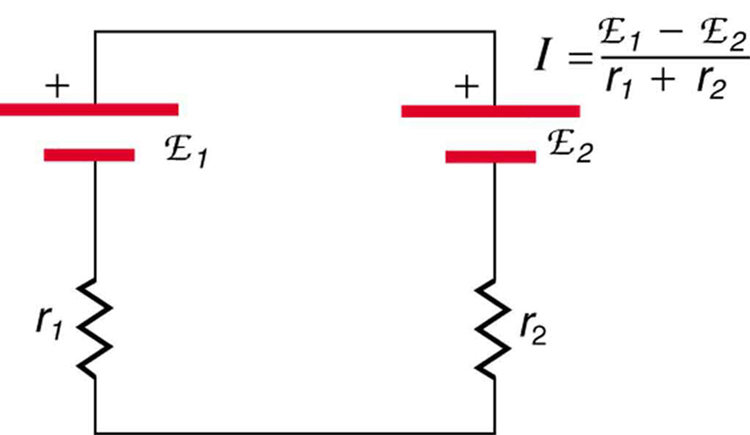
If the series connection of two voltage sources is made into a complete circuit with the emfs in opposition, then a current of magnitude flows. See [link] , for example, which shows a circuit exactly analogous to the battery charger discussed above. If two voltage sources in series with emfs in the same sense are connected to a load , as in [link] , then flows.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?