| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
The information presented in this section supports the following AP® learning objectives and science practices:

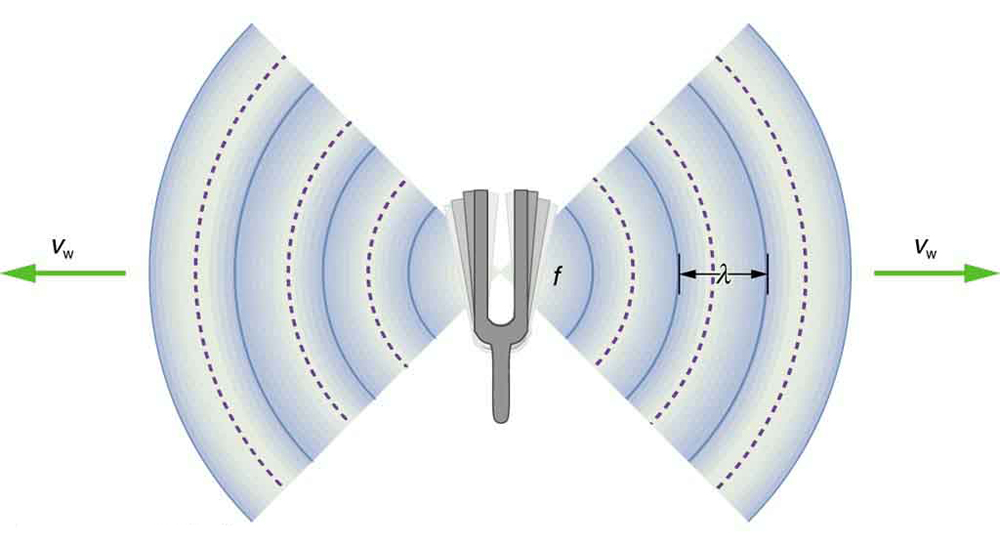
Sound, like all waves, travels at a certain speed and has the properties of frequency and wavelength. You can observe direct evidence of the speed of sound while watching a fireworks display. The flash of an explosion is seen well before its sound is heard, implying both that sound travels at a finite speed and that it is much slower than light. You can also directly sense the frequency of a sound. Perception of frequency is called pitch . The wavelength of sound is not directly sensed, but indirect evidence is found in the correlation of the size of musical instruments with their pitch. Small instruments, such as a piccolo, typically make high-pitch sounds, while large instruments, such as a tuba, typically make low-pitch sounds. High pitch means small wavelength, and the size of a musical instrument is directly related to the wavelengths of sound it produces. So a small instrument creates short-wavelength sounds. Similar arguments hold that a large instrument creates long-wavelength sounds.
The relationship of the speed of sound, its frequency, and wavelength is the same as for all waves:
where is the speed of sound, is its frequency, and is its wavelength. The wavelength of a sound is the distance between adjacent identical parts of a wave—for example, between adjacent compressions as illustrated in [link] . The frequency is the same as that of the source and is the number of waves that pass a point per unit time.
[link] makes it apparent that the speed of sound varies greatly in different media. The speed of sound in a medium is determined by a combination of the medium’s rigidity (or compressibility in gases) and its density. The more rigid (or less compressible) the medium, the faster the speed of sound. This observation is analogous to the fact that the frequency of a simple harmonic motion is directly proportional to the stiffness of the oscillating object. The greater the density of a medium, the slower the speed of sound. This observation is analogous to the fact that the frequency of a simple harmonic motion is inversely proportional to the mass of the oscillating object. The speed of sound in air is low, because air is compressible. Because liquids and solids are relatively rigid and very difficult to compress, the speed of sound in such media is generally greater than in gases.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?