| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
The information presented in this section supports the following AP® learning objectives and science practices:
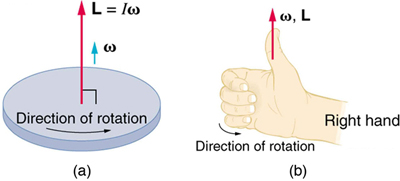
Angular momentum is a vector and, therefore, has direction as well as magnitude . Torque affects both the direction and the magnitude of angular momentum. What is the direction of the angular momentum of a rotating object like the disk in [link] ? The figure shows the right-hand rule used to find the direction of both angular momentum and angular velocity. Both and are vectors—each has direction and magnitude. Both can be represented by arrows. The right-hand rule defines both to be perpendicular to the plane of rotation in the direction shown. Because angular momentum is related to angular velocity by , the direction of is the same as the direction of . Notice in the figure that both point along the axis of rotation.
Now, recall that torque changes angular momentum as expressed by
This equation means that the direction of is the same as the direction of the torque that creates it. This result is illustrated in [link] , which shows the direction of torque and the angular momentum it creates.
Let us now consider a bicycle wheel with a couple of handles attached to it, as shown in [link] . (This device is popular in demonstrations among physicists, because it does unexpected things.) With the wheel rotating as shown, its angular momentum is to the woman's left. Suppose the person holding the wheel tries to rotate it as in the figure. Her natural expectation is that the wheel will rotate in the direction she pushes it—but what happens is quite different. The forces exerted create a torque that is horizontal toward the person, as shown in [link] (a). This torque creates a change in angular momentum in the same direction, perpendicular to the original angular momentum , thus changing the direction of but not the magnitude of . [link] shows how and add, giving a new angular momentum with direction that is inclined more toward the person than before. The axis of the wheel has thus moved perpendicular to the forces exerted on it , instead of in the expected direction.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?