| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A racehorse coming out of the gate accelerates from rest to a velocity of 15.0 m/s due west in 1.80 s. What is its average acceleration?

Strategy
First we draw a sketch and assign a coordinate system to the problem. This is a simple problem, but it always helps to visualize it. Notice that we assign east as positive and west as negative. Thus, in this case, we have negative velocity.
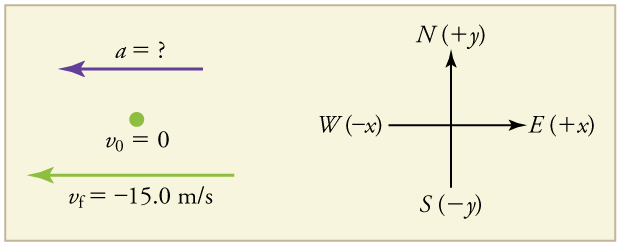
We can solve this problem by identifying and from the given information and then calculating the average acceleration directly from the equation .
Solution
1. Identify the knowns. , (the minus sign indicates direction toward the west), .
2. Find the change in velocity. Since the horse is going from zero to , its change in velocity equals its final velocity: .
3. Plug in the known values ( and ) and solve for the unknown .
Discussion
The minus sign for acceleration indicates that acceleration is toward the west. An acceleration of due west means that the horse increases its velocity by 8.33 m/s due west each second, that is, 8.33 meters per second per second, which we write as . This is truly an average acceleration, because the ride is not smooth. We shall see later that an acceleration of this magnitude would require the rider to hang on with a force nearly equal to his weight.
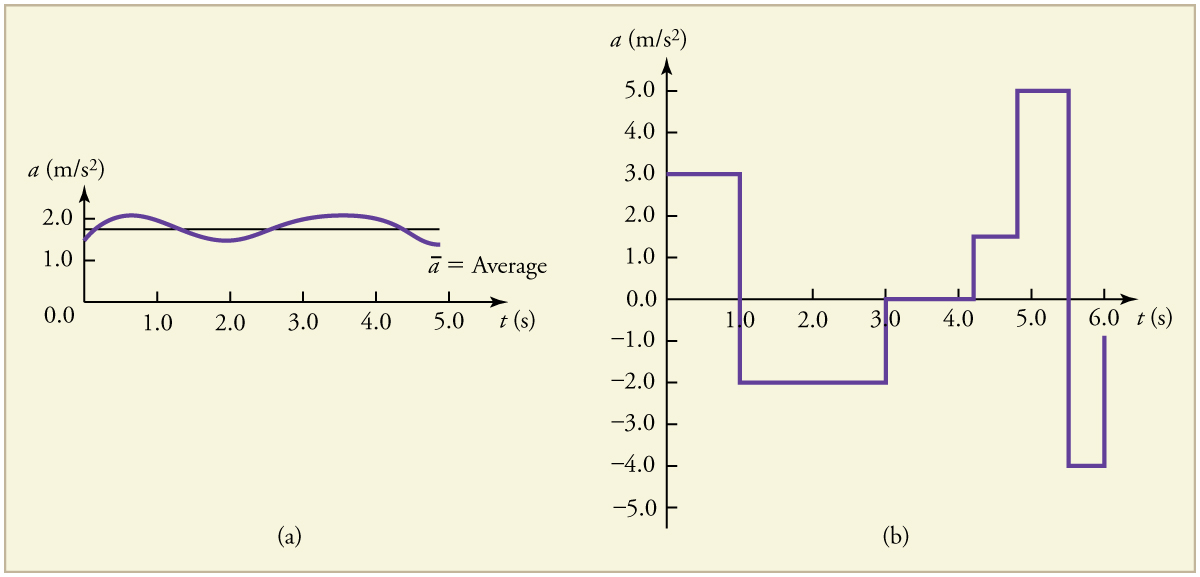
Instantaneous acceleration , or the acceleration at a specific instant in time , is obtained by the same process as discussed for instantaneous velocity in Time, Velocity, and Speed —that is, by considering an infinitesimally small interval of time. How do we find instantaneous acceleration using only algebra? The answer is that we choose an average acceleration that is representative of the motion. [link] shows graphs of instantaneous acceleration versus time for two very different motions. In [link] (a), the acceleration varies slightly and the average over the entire interval is nearly the same as the instantaneous acceleration at any time. In this case, we should treat this motion as if it had a constant acceleration equal to the average (in this case about ). In [link] (b), the acceleration varies drastically over time. In such situations it is best to consider smaller time intervals and choose an average acceleration for each. For example, we could consider motion over the time intervals from 0 to 1.0 s and from 1.0 to 3.0 s as separate motions with accelerations of and , respectively.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?