| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
All three rays appear to originate from the same point after being reflected, locating the upright virtual image behind the mirror and showing it to be larger than the object. (b) Makeup mirrors are perhaps the most common use of a concave mirror to produce a larger, upright image.
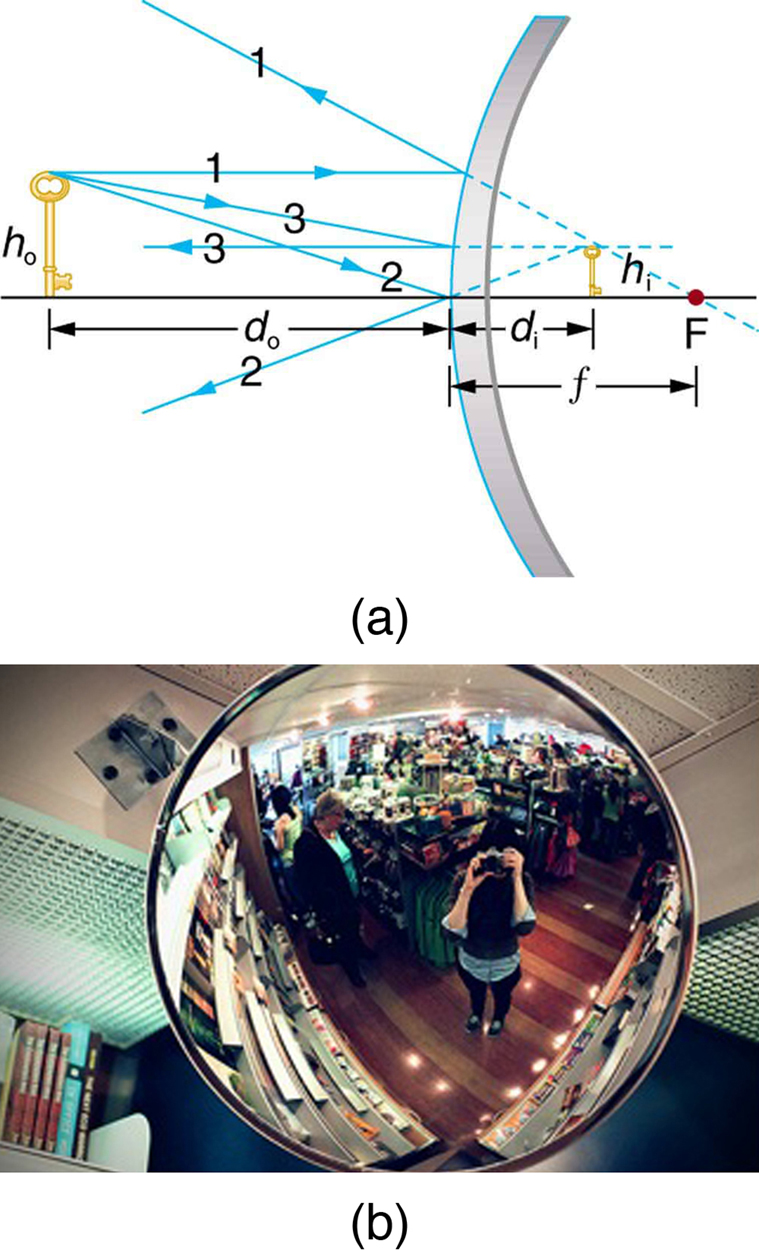
A convex mirror is a diverging mirror ( is negative) and forms only one type of image. It is a case 3 image—one that is upright and smaller than the object, just as for diverging lenses. [link] (a) uses ray tracing to illustrate the location and size of the case 3 image for mirrors. Since the image is behind the mirror, it cannot be projected and is thus a virtual image. It is also seen to be smaller than the object.
A keratometer is a device used to measure the curvature of the cornea, particularly for fitting contact lenses. Light is reflected from the cornea, which acts like a convex mirror, and the keratometer measures the magnification of the image. The smaller the magnification, the smaller the radius of curvature of the cornea. If the light source is 12.0 cm from the cornea and the image’s magnification is 0.0320, what is the cornea’s radius of curvature?
Strategy
If we can find the focal length of the convex mirror formed by the cornea, we can find its radius of curvature (the radius of curvature is twice the focal length of a spherical mirror). We are given that the object distance is and that . We first solve for the image distance , and then for .
Solution
. Solving this expression for gives
Entering known values yields
Substituting known values,
This must be inverted to find :
The radius of curvature is twice the focal length, so that
Discussion
Although the focal length of a convex mirror is defined to be negative, we take the absolute value to give us a positive value for . The radius of curvature found here is reasonable for a cornea. The distance from cornea to retina in an adult eye is about 2.0 cm. In practice, many corneas are not spherical, complicating the job of fitting contact lenses. Note that the image distance here is negative, consistent with the fact that the image is behind the mirror, where it cannot be projected. In this section’s Problems and Exercises, you will show that for a fixed object distance, the smaller the radius of curvature, the smaller the magnification.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?