| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The first law of thermodynamics is actually the law of conservation of energy stated in a form most useful in thermodynamics. The first law gives the relationship between heat transfer, work done, and the change in internal energy of a system.
Heat transfer ( ) and doing work ( ) are the two everyday means of bringing energy into or taking energy out of a system. The processes are quite different. Heat transfer, a less organized process, is driven by temperature differences. Work, a quite organized process, involves a macroscopic force exerted through a distance. Nevertheless, heat and work can produce identical results. For example, both can cause a temperature increase. Heat transfer into a system, such as when the Sun warms the air in a bicycle tire, can increase its temperature, and so can work done on the system, as when the bicyclist pumps air into the tire. Once the temperature increase has occurred, it is impossible to tell whether it was caused by heat transfer or by doing work. This uncertainty is an important point. Heat transfer and work are both energy in transit—neither is stored as such in a system. However, both can change the internal energy of a system. Internal energy is a form of energy completely different from either heat or work.
We can think about the internal energy of a system in two different but consistent ways. The first is the atomic and molecular view, which examines the system on the atomic and molecular scale. The internal energy of a system is the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of its atoms and molecules. Recall that kinetic plus potential energy is called mechanical energy. Thus internal energy is the sum of atomic and molecular mechanical energy. Because it is impossible to keep track of all individual atoms and molecules, we must deal with averages and distributions. A second way to view the internal energy of a system is in terms of its macroscopic characteristics, which are very similar to atomic and molecular average values.
Macroscopically, we define the change in internal energy to be that given by the first law of thermodynamics:
Many detailed experiments have verified that , where is the change in total kinetic and potential energy of all atoms and molecules in a system. It has also been determined experimentally that the internal energy of a system depends only on the state of the system and not how it reached that state . More specifically, is found to be a function of a few macroscopic quantities (pressure, volume, and temperature, for example), independent of past history such as whether there has been heat transfer or work done. This independence means that if we know the state of a system, we can calculate changes in its internal energy from a few macroscopic variables.
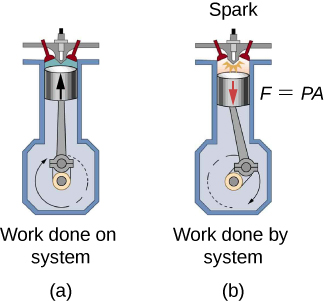
In a previous chapter, temperature was related to the average kinetic energy of the individual molecules in the material. This relates to the concept of total internal energy in a system. Recall that the total internal energy of a system is defined as the sum of all the kinetic energies of all the elements of the system, plus the sum of all the potential energies of interactions between all of the pairs of elements in the system. For example, consider an internal combustion engine utilizing a piston in a cylinder. First, the piston compresses the gas in the cylinder, forcing the molecules closer to each other and changing their potential energy by an outside force doing work on the system. This is the compression stroke, [link] (b). Then fuel is burned in the cylinder, raising the temperature and hence kinetic energy of all of the molecules. Therefore, the internal energy of the system has had chemical potential energy converted into kinetic energy. This occurs between the compression and power strokes in the figure. Then the piston is pushed back out, using some of the internal energy of the system to do work on an outside system, as shown in the power stroke in the figure.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?